Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text
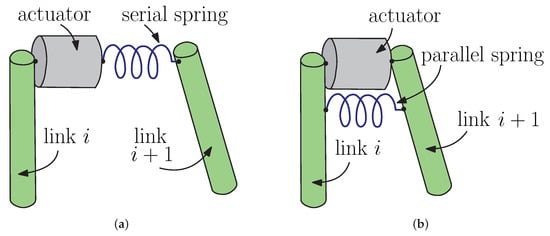
Energy saving in robotic and mechatronic systems is becoming an evermore important topic in both industry and academia. One strategy to reduce the energy consumption, especially for cyclic tasks, is exploiting natural motion. We define natural motion as the system response caused by the conversion of potential elastic energy into kinetic energy. This motion can be both a forced response assisted by a motor or a free response. The application of the natural motion concepts allows for energy saving in tasks characterized by repetitive or cyclic motion. This review paper proposes a classification of several approaches to natural motion, starting from the compliant elements and the actuators needed for its implementation. Then several approaches to natural motion are discussed based on the trajectory followed by the system, providing useful information to the researchers dealing with natural motion.
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, rated speed
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, scp 6664

Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, gas hupe dose
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, rule 63 urban dictionary
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, g1 f1800

Applied Sciences An Open Access Journal from MDPI

Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, define empathetic

Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, Hemming Tool
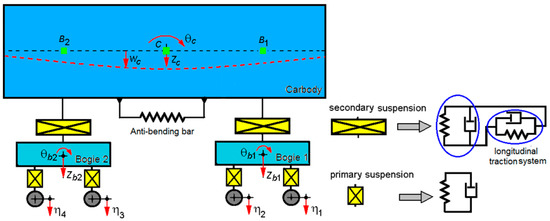
Savings StarApplied Sciences, Free Full-Text, methods of reducing vibration
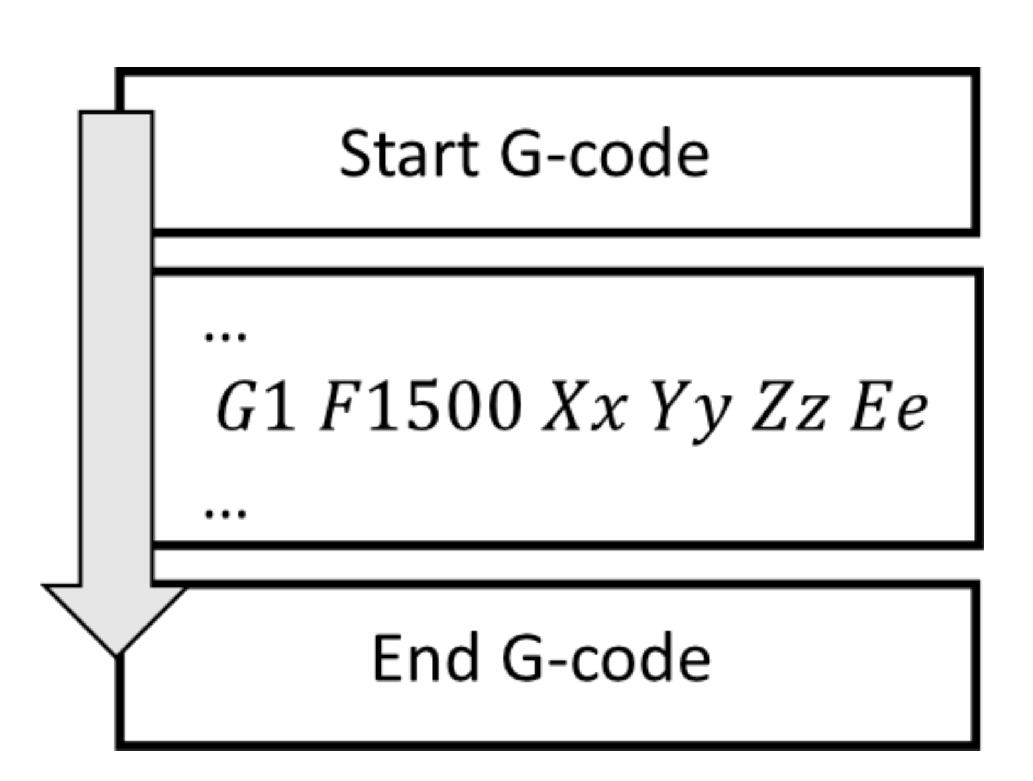
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, g1 f1500

Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, rated output

Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, rated output









