Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text
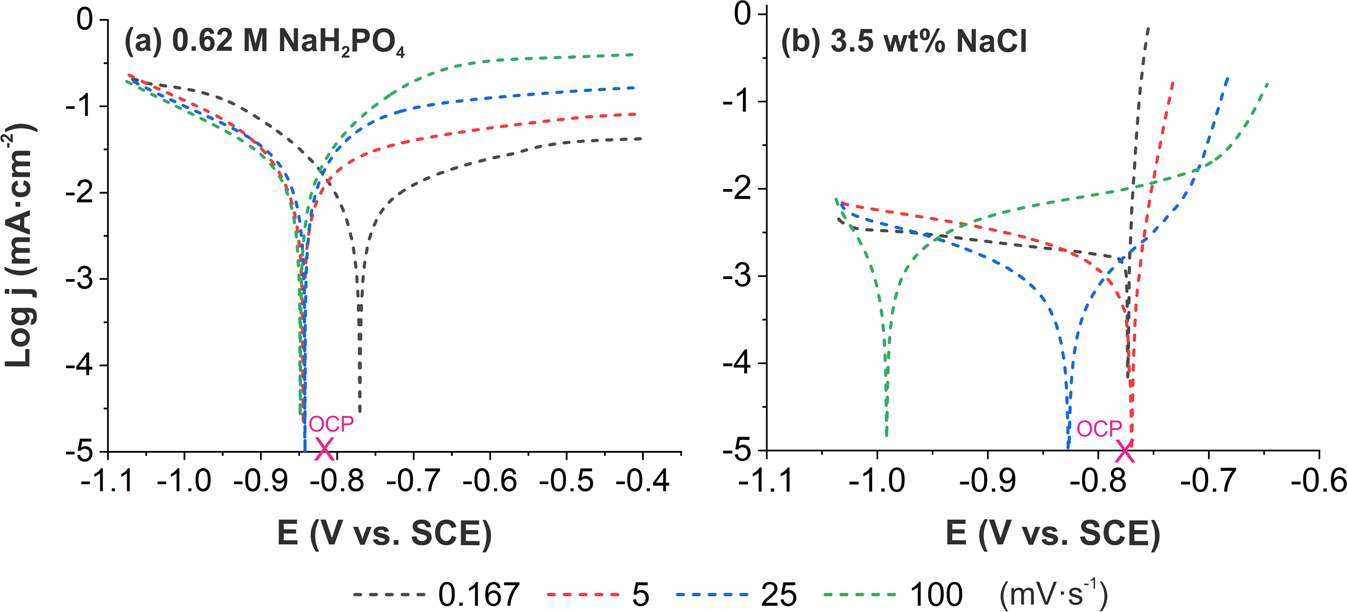
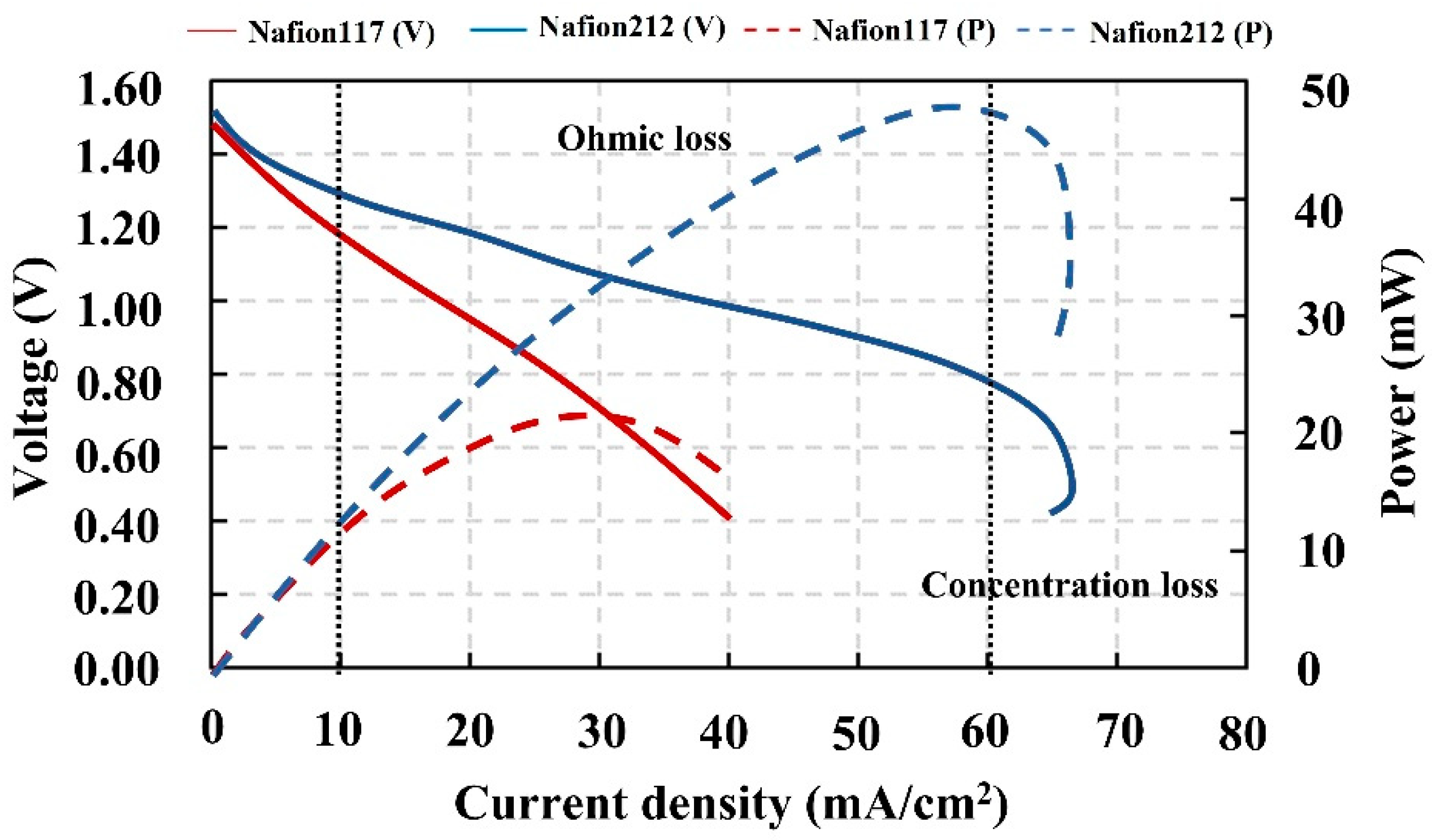
This article proposes the demonstration and deployment of a hand-tailored vanadium redox flow battery test station to investigate the effect of applied voltages on charging performance for electrolyte preparation and the effect of reactant flow rates on the balance of system capacity. Herein, the two different specifications of membranes and a number of electrode layers playing pivotal roles in the discharging characteristics of the VRFB were observed as well. Results indicated that 1.70 V of the charging voltage was suitable, when optimized voltage was considered from charging time, current, and the mole of electrons. The optimized flow rate (10 mL/min) must be controlled since it corresponds to mass transfer and electrolyte diffusion, resulting in reaction ability on electrode surfaces. The number of layers influenced active areas and the diffusion of electrolytes. Nafion 212 provided superior performance to Nafion 117, because it possessed lower ohmic resistance and allowed for easier proton transfer.
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, driving simulator 2009

Cell-Free Synthetic Biology
Find VA Research Articles and Projects in PubMed Central and NIH RePORTER

Applied Sciences An Open Access Journal from MDPI

Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, script king legacy mobile sem
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, Emulsion

Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, g1 f1500

Tianjin Sino-German University of Applied Science, Full Free Scholarship

Sources for technology and business insights explained, part 4/7: Scientific publications - Mergeflow