Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text
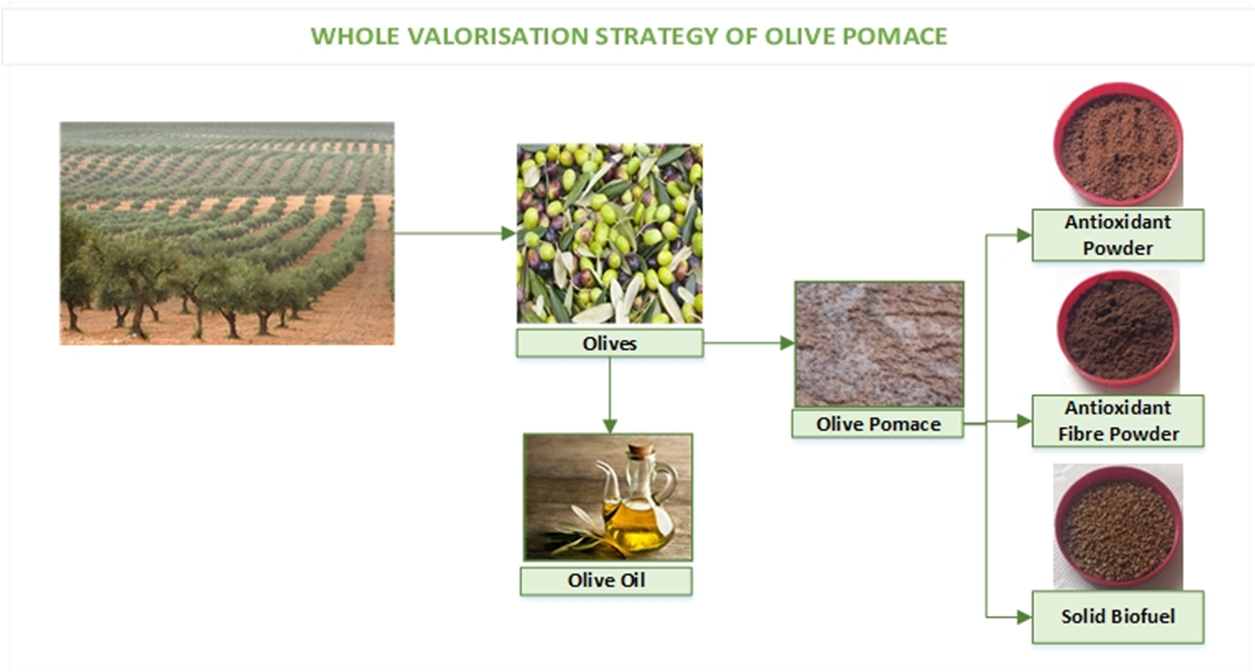
Olive pomace management represents a great concern to the olive oil industry. This work focused on the development of a “zero waste” strategy for olive pomace based on a fractionation approach resulting in the obtention of different value-added fractions. The physicochemical composition of edible fractions obtained (liquid and pulp) was analysed. The potential use as a solid biofuel of the non-edible fraction (stones) was evaluated. High amounts of hydroxytyrosol (513.61–625.76 mg/100 g dry weight) were present in the liquid fraction. Pulp fraction was demonstrated to be a good source of fibre (53–59% dry weight) with considerable antioxidant activity both from free and bound phenolics. The stones fraction exhibited substantial high heating values (18.65–18.94 megajoule (MJ/kg). All these results support the added value of the olive pomace fractions combining the biofuel potential from the stones fraction and the functional food ingredients’ potential both from liquid and pulp fractions. The present methodology seems to be a feasible whole valorisation approach to achieve the circularity in the olive oil sector, prioritising obtaining high over low added-value products.

Applied Sciences An Open Access Journal from MDPI
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, driving simulator 2009

Applied Sciences An Open Access Journal from MDPI
Update: New Web of Science and LibKey Nomad – Libraries News
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, define empathetic

Sources for technology and business insights explained, part 4/7
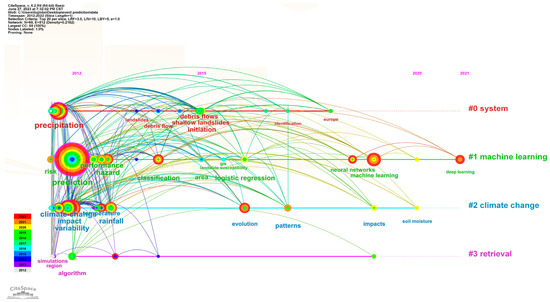
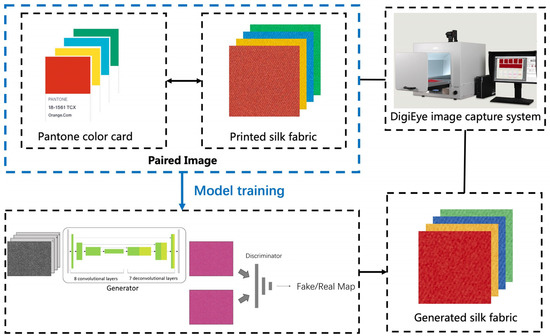
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, Synthetic Dye
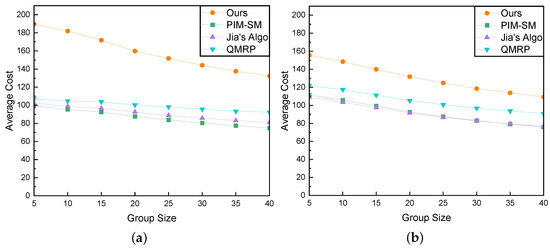
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, rated speed

Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, g1 f1800

Sport Performance & Science Reports
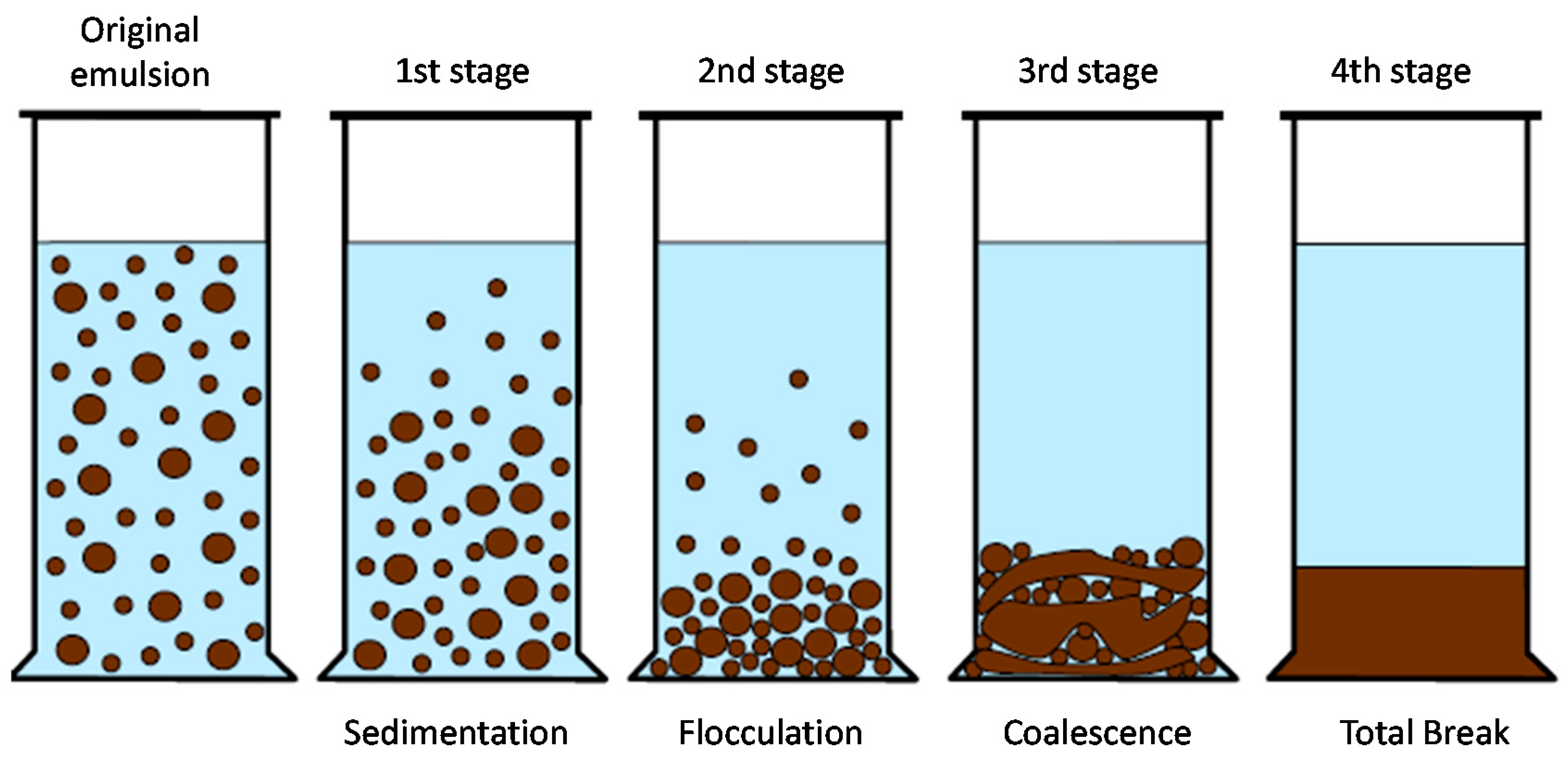
Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, Emulsion

Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text, gas hupe dose

Applied Science Fiction Vector Logo - Download Free SVG Icon









