The cardiac surgery–associated neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (CSA-NGAL) score: A potential tool to monitor acute tubular damage - ScienceDirect

Distribution of the patients according to diagnosis with pNGAL and eGFR

PDF) Plasma Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin and Worsening Renal Function During Everolimus Therapy After Heart Transplantation

Usefulness and limitations of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in the assessment of kidney diseases
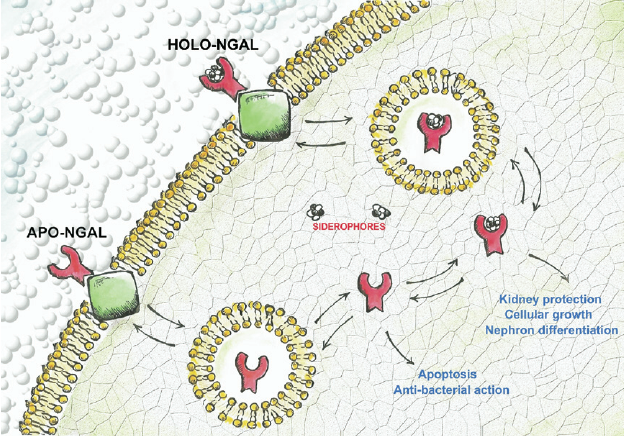
The origin of plasma neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in cardiac surgery, BMC Nephrology
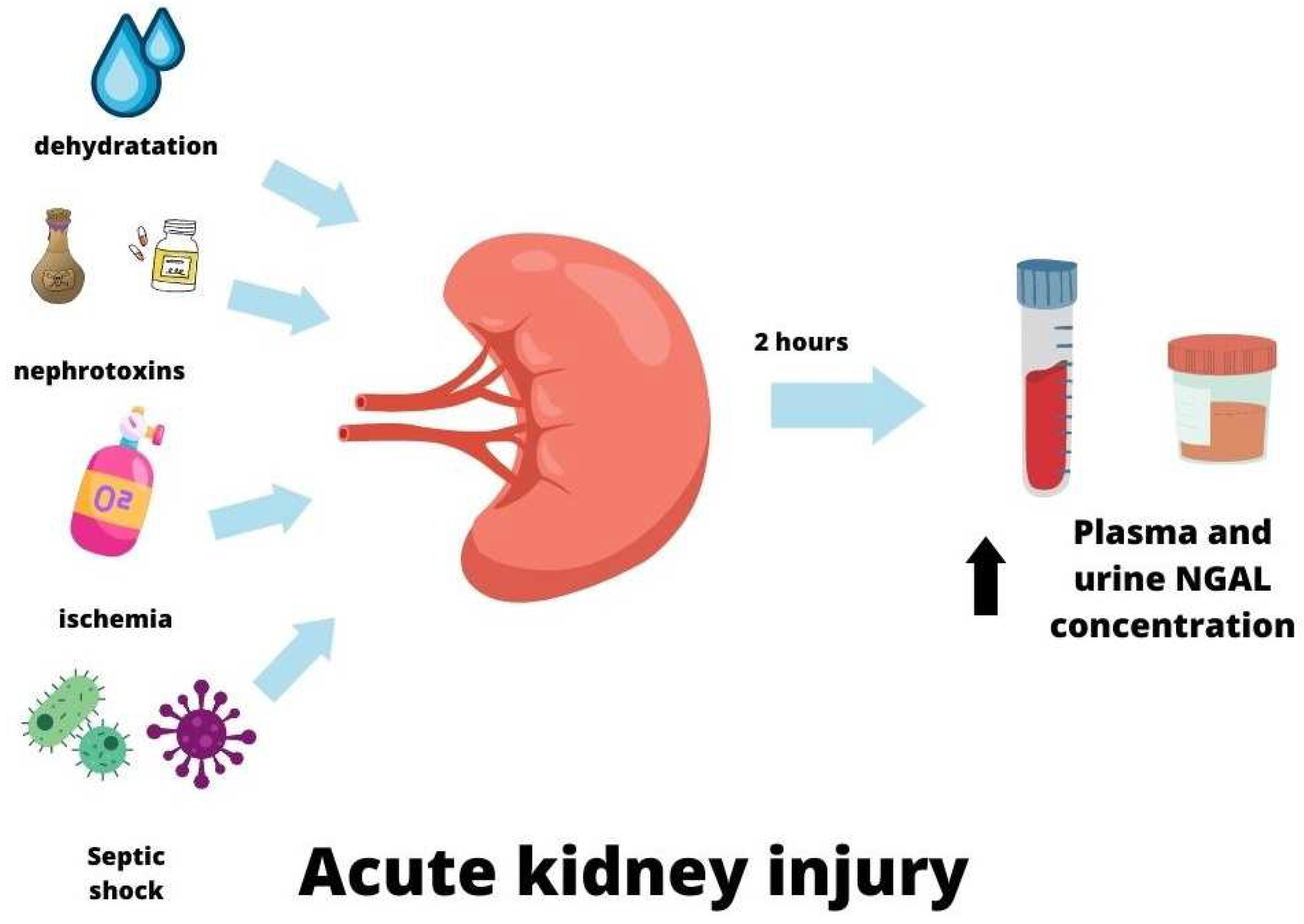
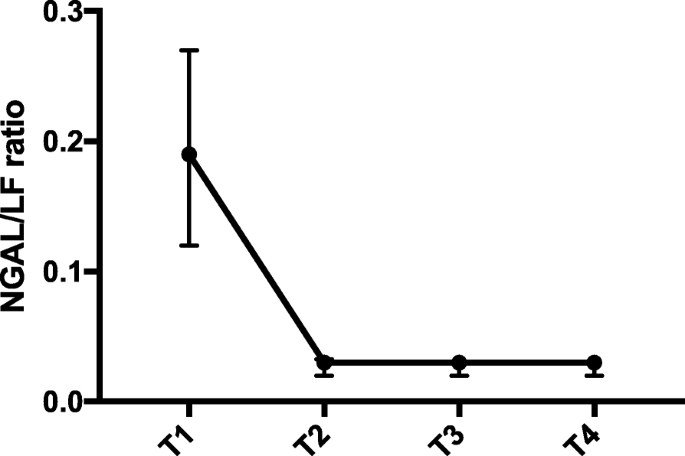
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin Measured on Clinical Laboratory Platforms for the Prediction of Acute Kidney Injury and the Associated Need for Dialysis Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis - ScienceDirect

Delayed Graft Function in the Kidney Transplant - American Journal of Transplantation
Urine Neutrophil Gelatinase-associated Lipocalin (NGAL) for Prediction of Persistent AKI and Major Adverse Kidney Events

Oral abstracts - 2022 - Pediatric Transplantation - Wiley Online Library
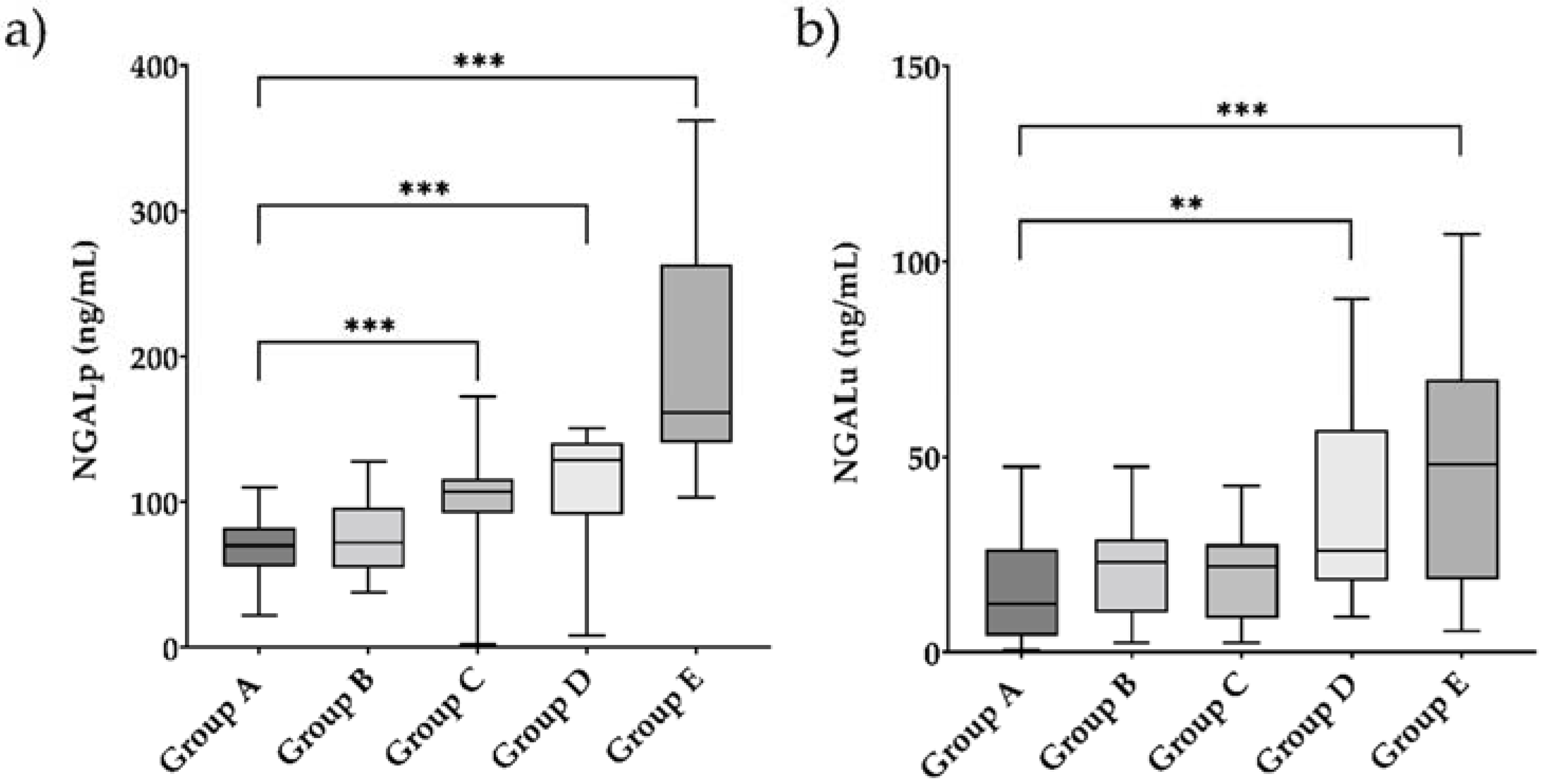
Endocrines, Free Full-Text
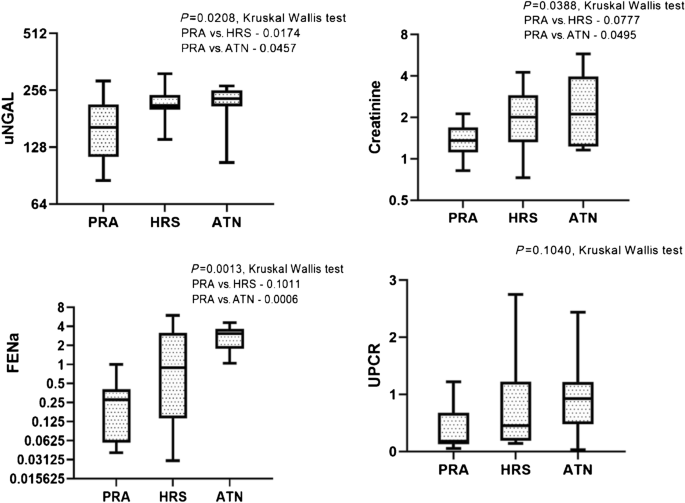
Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker of acute kidney injury and prognosis in decompensated chronic liver disease: A prospective study

PDF) Activation of the angiotensin II receptor promotes autophagy in renal proximal tubular cells and affords protection from ischemia/reperfusion injury

The cardiac surgery–associated neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin ( CSA-NGAL) score: A potential tool to monitor acute tubular damage - ScienceDirect

Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and plasma IL-6 in discontinuation of continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration for severe acute kidney injury: a multicenter prospective observational study, Annals of Intensive Care
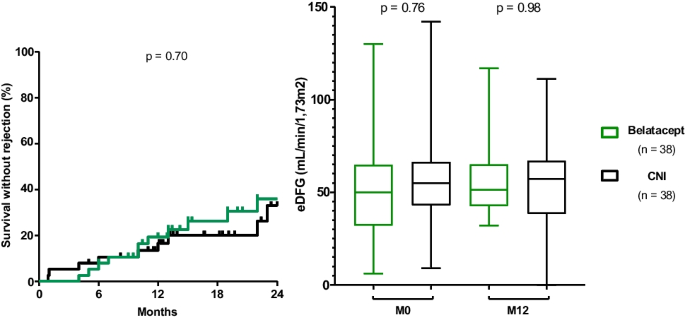
Abstracts of the 55th ESPN Annual Meeting, Vilnius, Lithuania