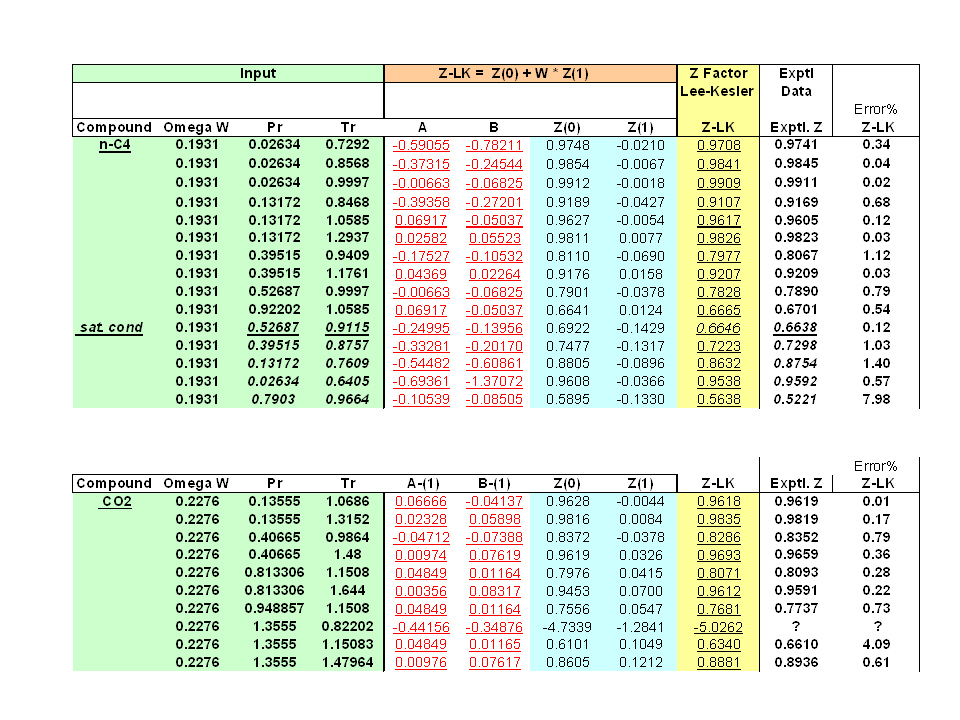
Compressibility factor z versus 100/V, for several values of
Download scientific diagram | Compressibility factor z versus 100/V, for several values of Pressure and 222 Temperature, for CO2. 223 224 The optimum placement of the compressor in the diagram of Figure 4 is achieved at 225 temperatures and pressures below the critical point. The increase of the temperature or 226 the pressure above the critical point leads to big changes in the compressibility factor. In 227 general, small changes in temperature and/or pressure around the critical point involves 228 big thermodynamic changes. This paper analyzes power cycles with the compressor 229 working in this region. We will call the region around the critical point "pericritical 230 region", where peri stands for "around" in Latin. 231 232 from publication: Thermodynamic mapping of power cycles working around the critical point | A new thermodynamic coefficient, called logarithmic factor of isobaric expansion, is defined for a better guidance in the cycle characterization of regenerative cycles working totally or partially at supercritical conditions. The logarithmic factor of isobaric expansion | Cycling, Thermodynamics and Work | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

PDF) Thermodynamic mapping of power cycles working around the critical point
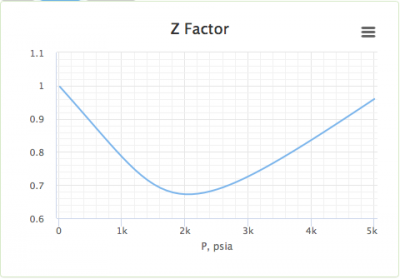
Is z (compressibility factor) vs P (pressure) graph drawn by

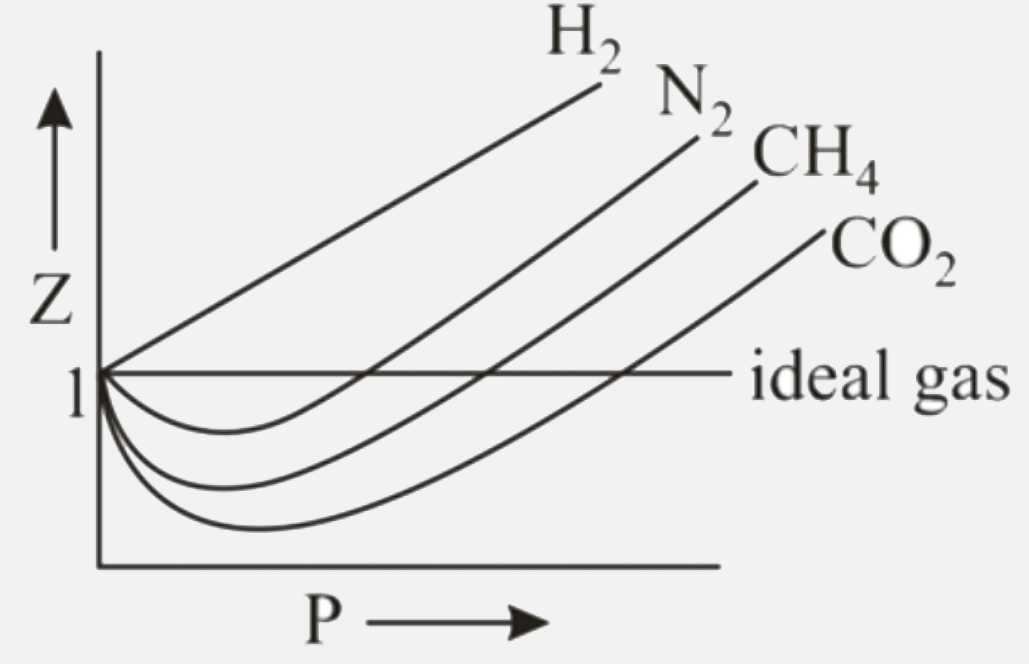
Compressibility factor - Wikipedia

Compressibility factor - Wikipedia

physical chemistry - Is the compressibility factor smaller or

Gas compressibility factor Z: Ideal gas vs Real gas
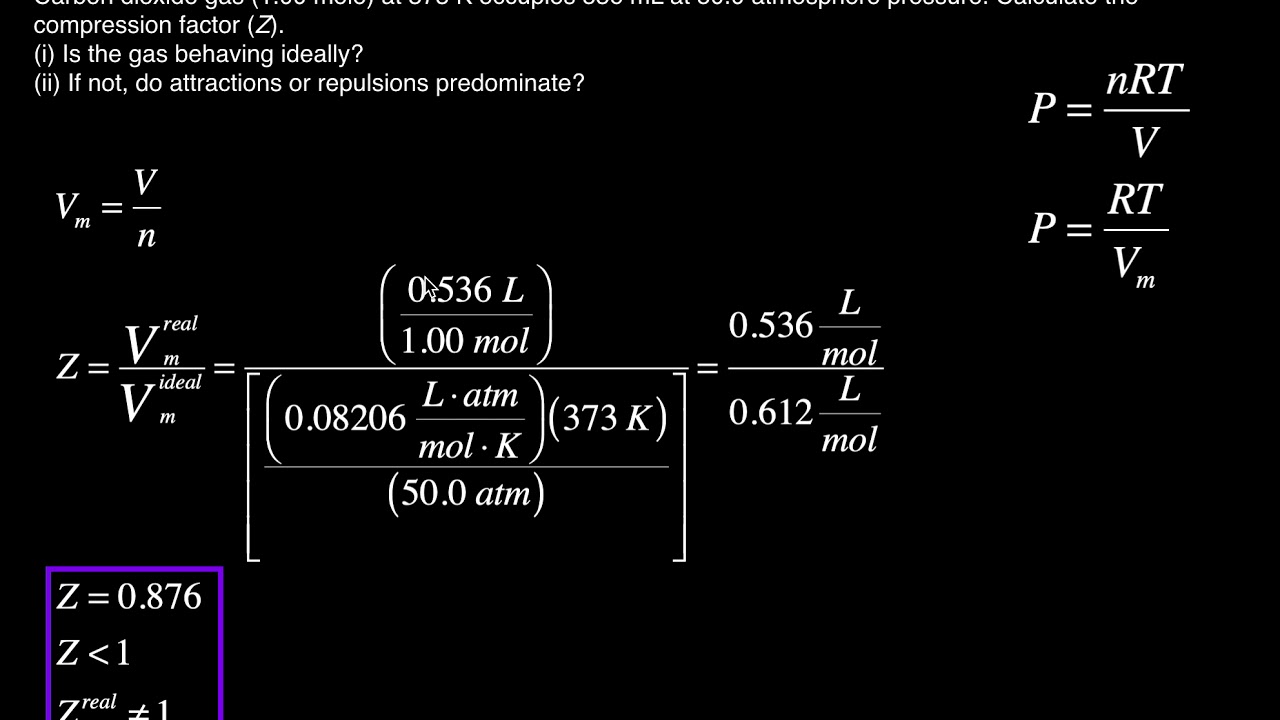
Real Gas Behavior The Compression Factor (Z) [Example #2]

Compressibility factor z versus 100/V, for several values of Pressure

Jose MARTINEZ-VAL, Chair Professor of Thermal Engineering, Ph.D. Engineering, Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Madrid, UPM, Institute of Nuclear Fusion IFN (DENIM)

Compressibility Factor - an overview

Compressibility factor, Z of a gas is given as Z = pV / nRTi What

e Compressibility factor (Z) for hydrogen WRT pressure and

1.7: Connecting the van der Waals and the viral equations: the

Deviation of Real Gases from Ideal Gas Behaviour - GeeksforGeeks
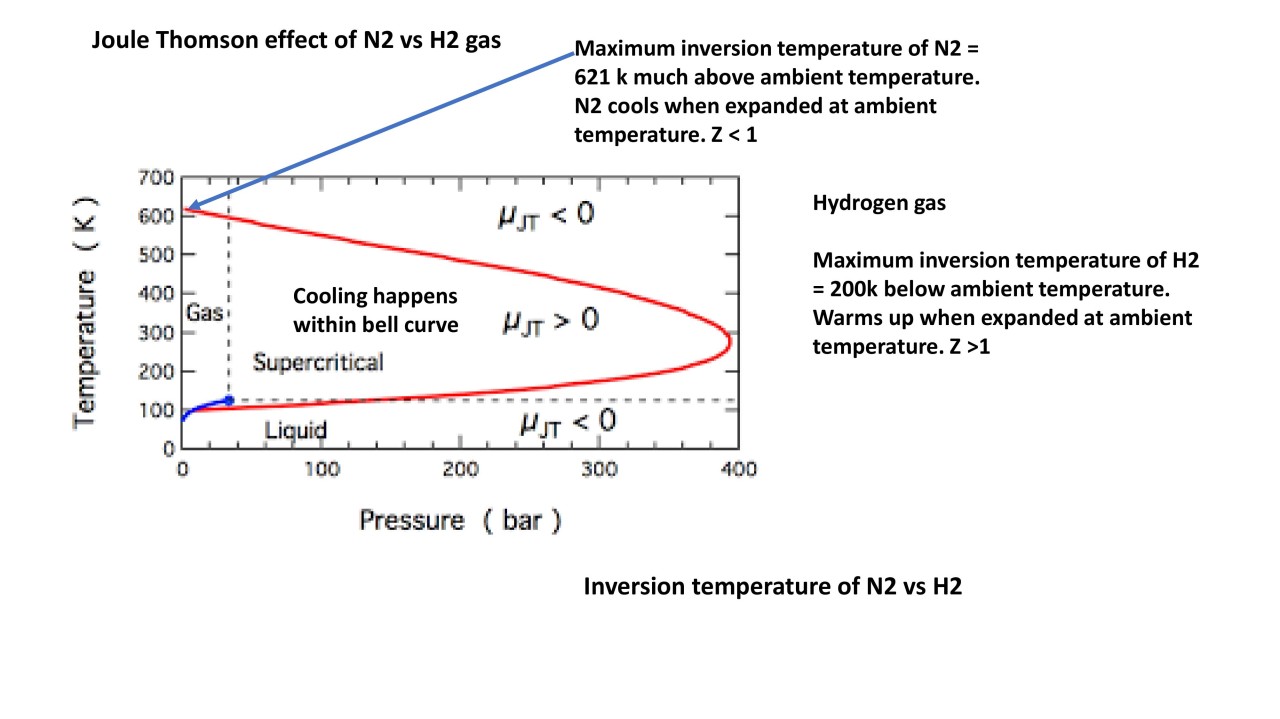
Joule Thomson effect [JT]: A short review