Genetic variants associated with breast size also influence breast cancer risk, BMC Medical Genetics
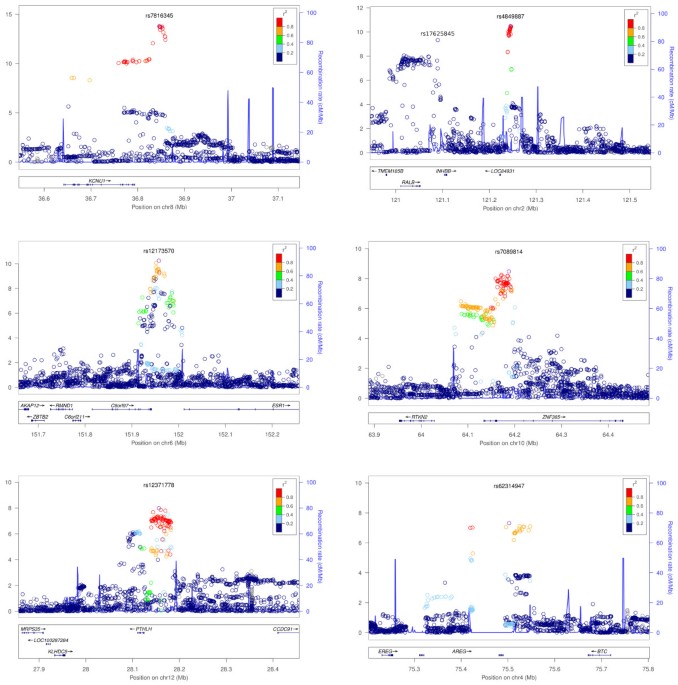
Background While some factors of breast morphology, such as density, are directly implicated in breast cancer, the relationship between breast size and cancer is less clear. Breast size is moderately heritable, yet the genetic variants leading to differences in breast size have not been identified. Methods To investigate the genetic factors underlying breast size, we conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of self-reported bra cup size, controlling for age, genetic ancestry, breast surgeries, pregnancy history and bra band size, in a cohort of 16,175 women of European ancestry. Results We identified seven single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) significantly associated with breast size (p<5·10−8): rs7816345 near ZNF703, rs4849887 and (independently) rs17625845 flanking INHBB, rs12173570 near ESR1, rs7089814 in ZNF365, rs12371778 near PTHLH, and rs62314947 near AREG. Two of these seven SNPs are in linkage disequilibrium (LD) with SNPs associated with breast cancer (those near ESR1 and PTHLH), and a third (ZNF365) is near, but not in LD with, a breast cancer SNP. The other three loci (ZNF703, INHBB, and AREG) have strong links to breast cancer, estrogen regulation, and breast development. Conclusions These results provide insight into the genetic factors underlying normal breast development and show that some of these factors are shared with breast cancer. While these results do not directly support any possible epidemiological relationships between breast size and cancer, this study may contribute to a better understanding of the subtle interactions between breast morphology and breast cancer risk.

知乎日报- 知乎

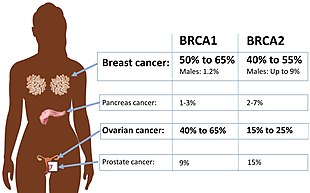
Inherited Breast Cancer Syndromes
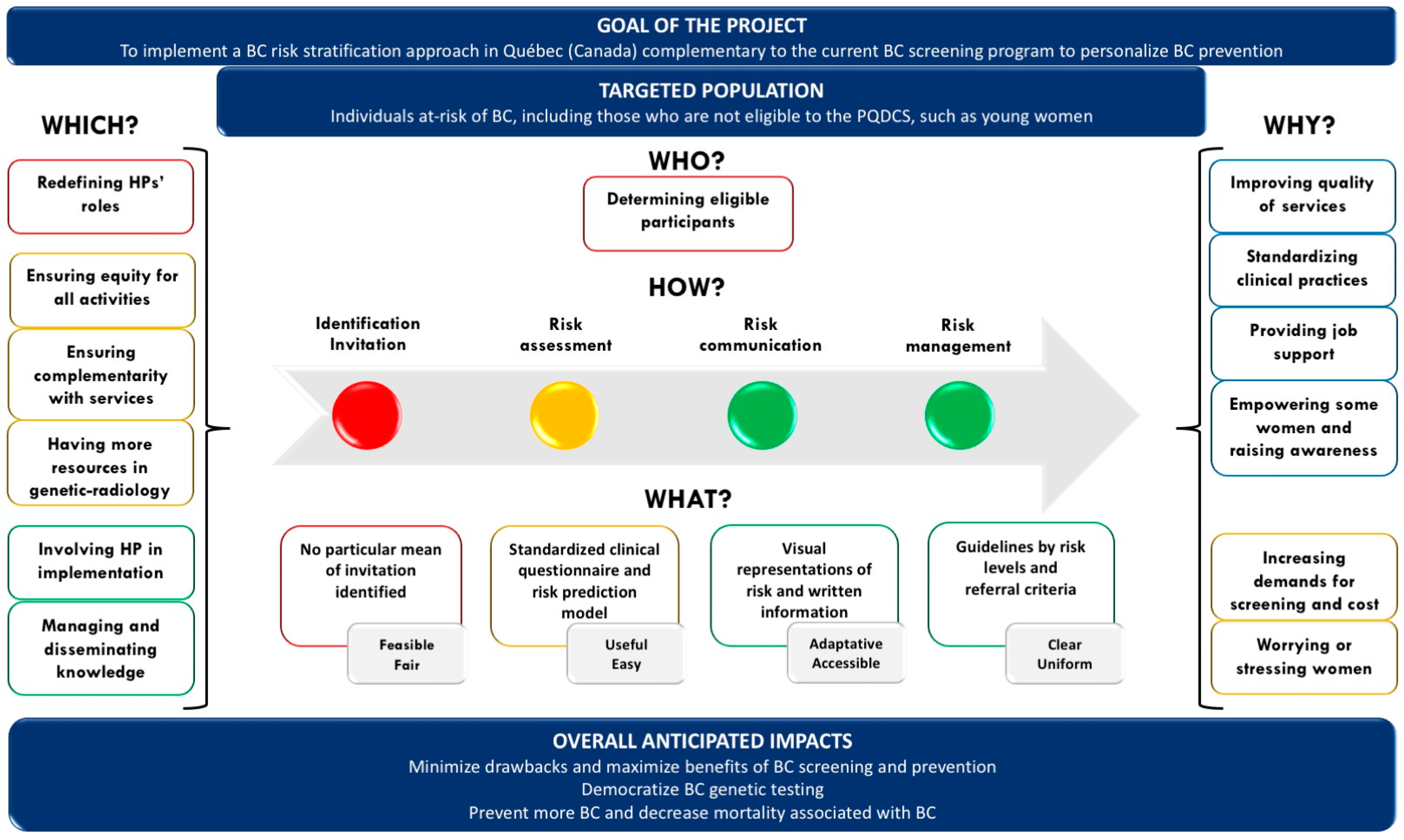
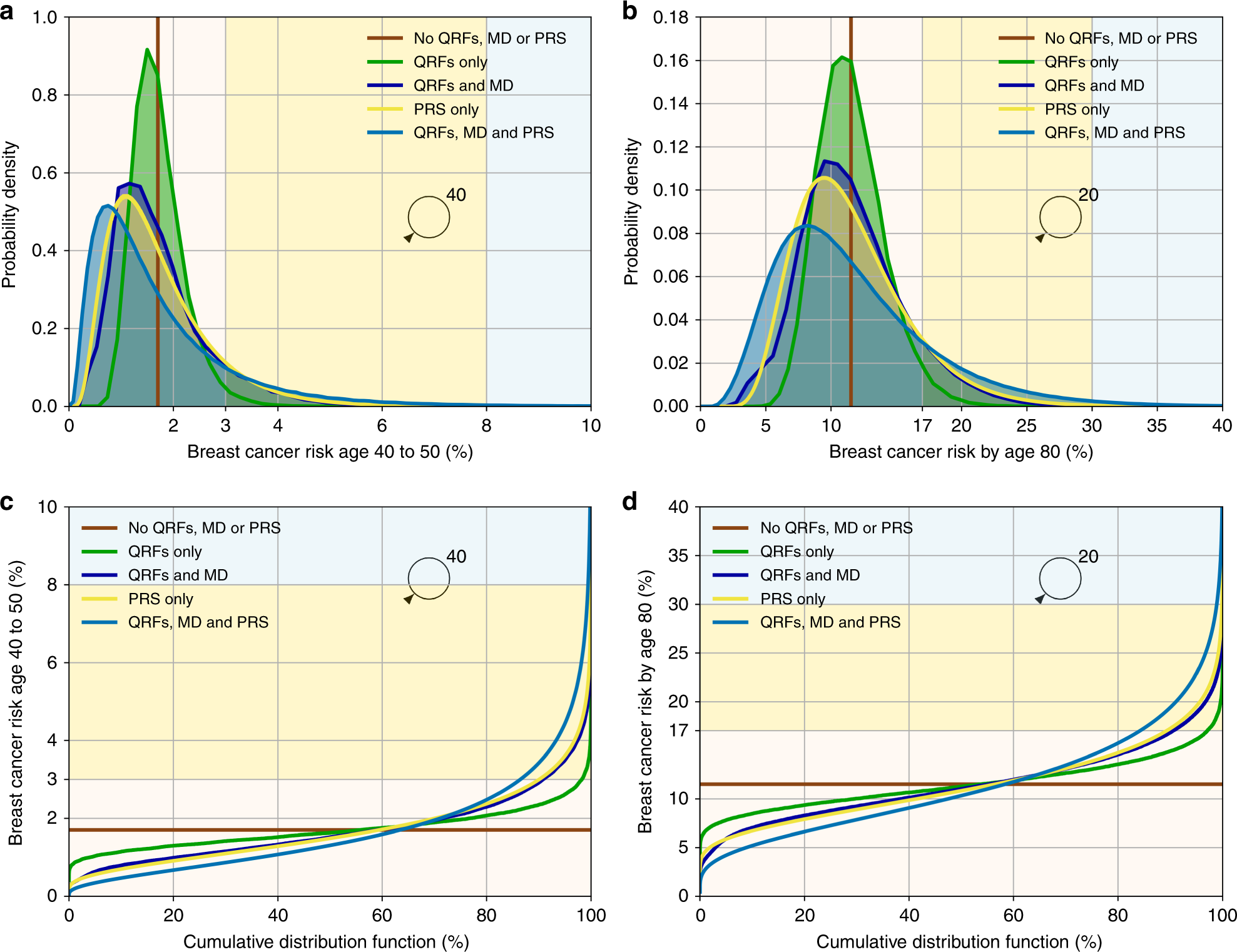
JPM, Free Full-Text

Breast cancer - Wikipedia

ESR1 polymorphism (rs2234693) influences femoral bone mass in patients with Turner syndrome in: Endocrine Connections Volume 8 Issue 11 (2019)

Genetic association studies of alterations in protein function expose recessive effects on cancer predisposition

Large-scale genotyping identifies a new locus at 22q13.2 associated with female breast size. - Abstract - Europe PMC

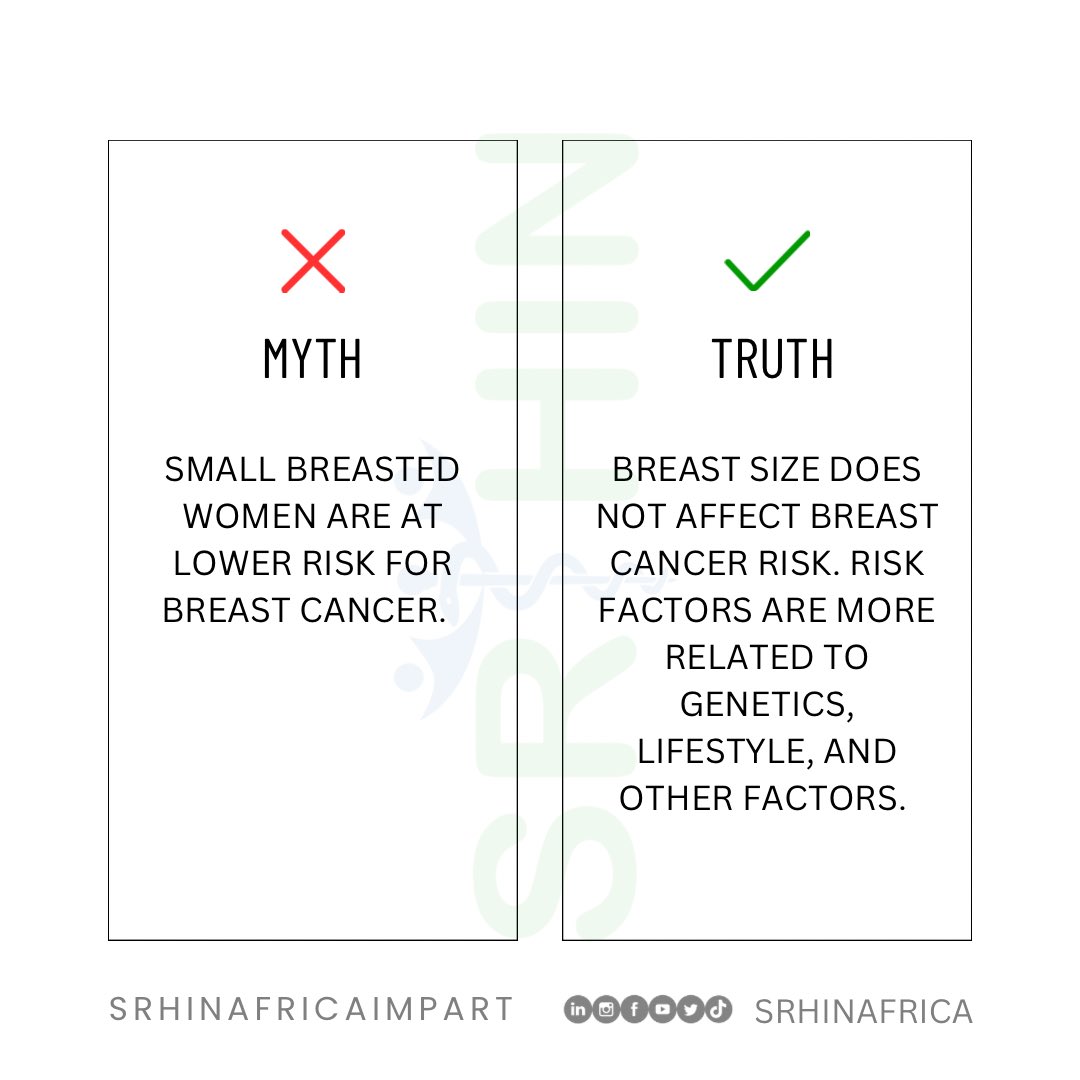
还在被丰胸谣言所骗吗?胸部大小超56%由先天基因决定! - 知乎

Genetic insights into carbohydrate sulfotransferase 8 and its impact on the immunotherapy efficacy of cancer - ScienceDirect

知乎日报- 知乎

How does re-classification of variants of unknown significance (VUS) impact the management of patients at risk for hereditary breast cancer?, BMC Medical Genomics

2012 in science - Wikipedia