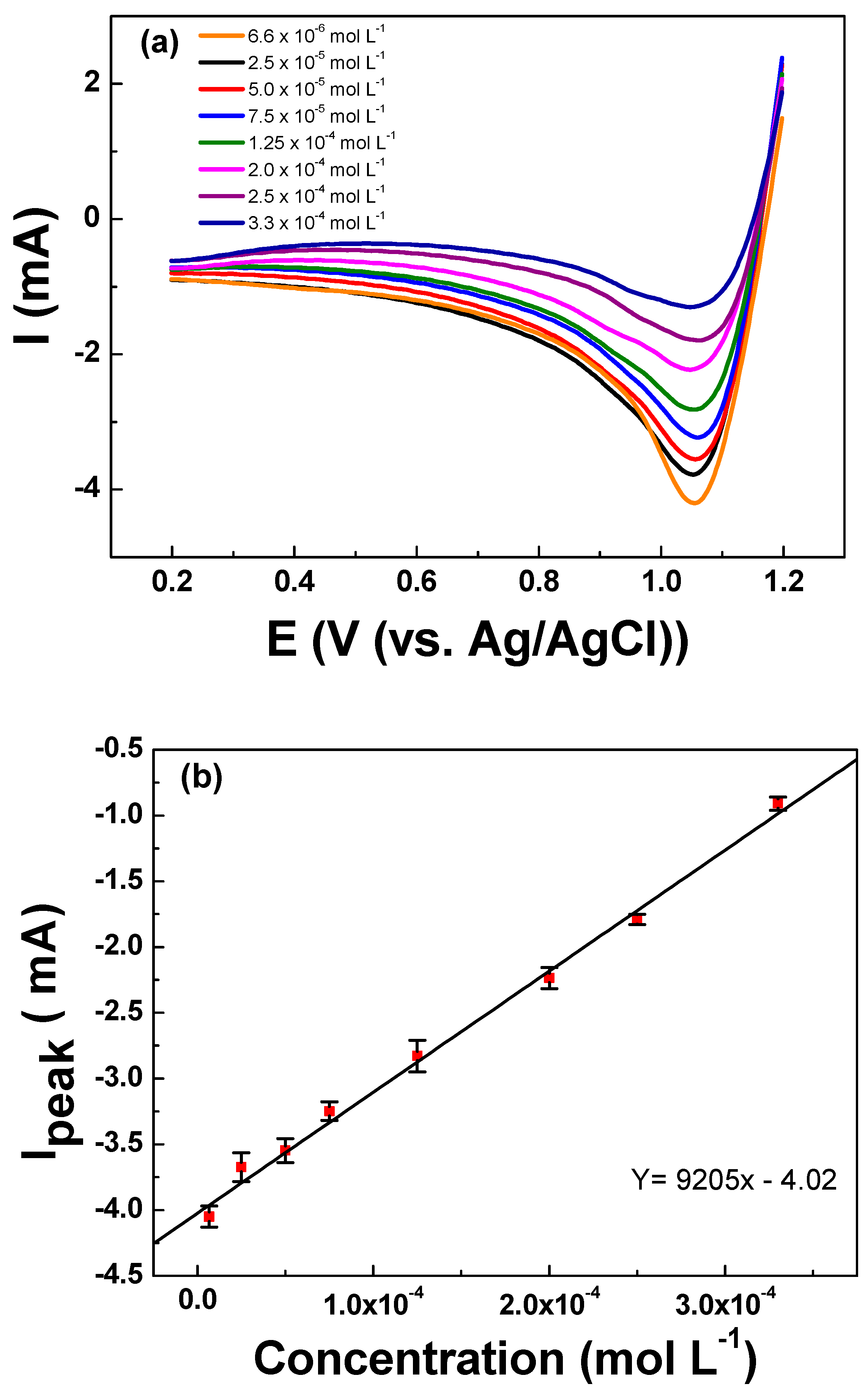
Investigation of Electrochemical Pitting Corrosion by Linear Sweep Voltammetry: A Fast and Robust Approach
Generally, impedance spectroscopy, cyclic voltammetry and polarographic methods are used to study the pitting corrosion of steel, stainless steel and many different alloys. But one can also use linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) to investigate the pitting corrosion phenomenon. LSV is having many advantages over other traditional methods; but more research should take place in this area to foreshorten the lacuna. It is an important electrochemical method that involves solid electrode, fixed potential and fast scan rate. The advantage of using LSV in determining the pitting corrosion is less time required in the order of few seconds, and there is no need of keeping the samples in NaCl or any other electrolytes for many months.

Linear Sweep Voltammetry - an overview
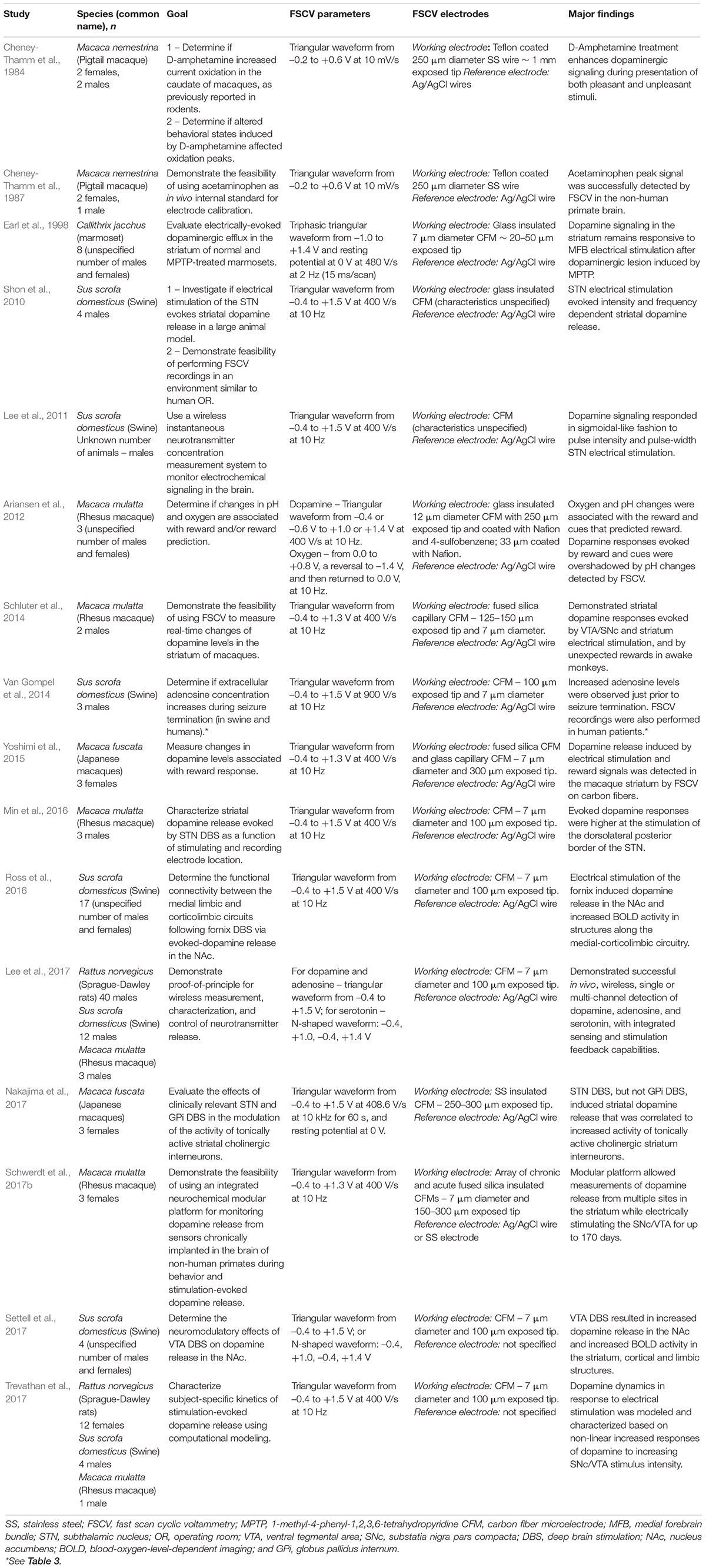
Frontiers Defining a Path Toward the Use of Fast-Scan Cyclic

The Correlation Between Electrochemical Behavior and Neutral Salt Fog Corrosion on TCP Coated AA2024

Interface Vol. 26, No. 3, Fall 2017 by The Electrochemical Society - Issuu

Linear Sweep Voltammetry - an overview

Recent Progress in Electrolyte Development and Design Strategies for Next‐Generation Potassium‐Ion Batteries - Verma - 2021 - Batteries & Supercaps - Wiley Online Library

Optical microscope images of (a) duplex stainless steel and (b
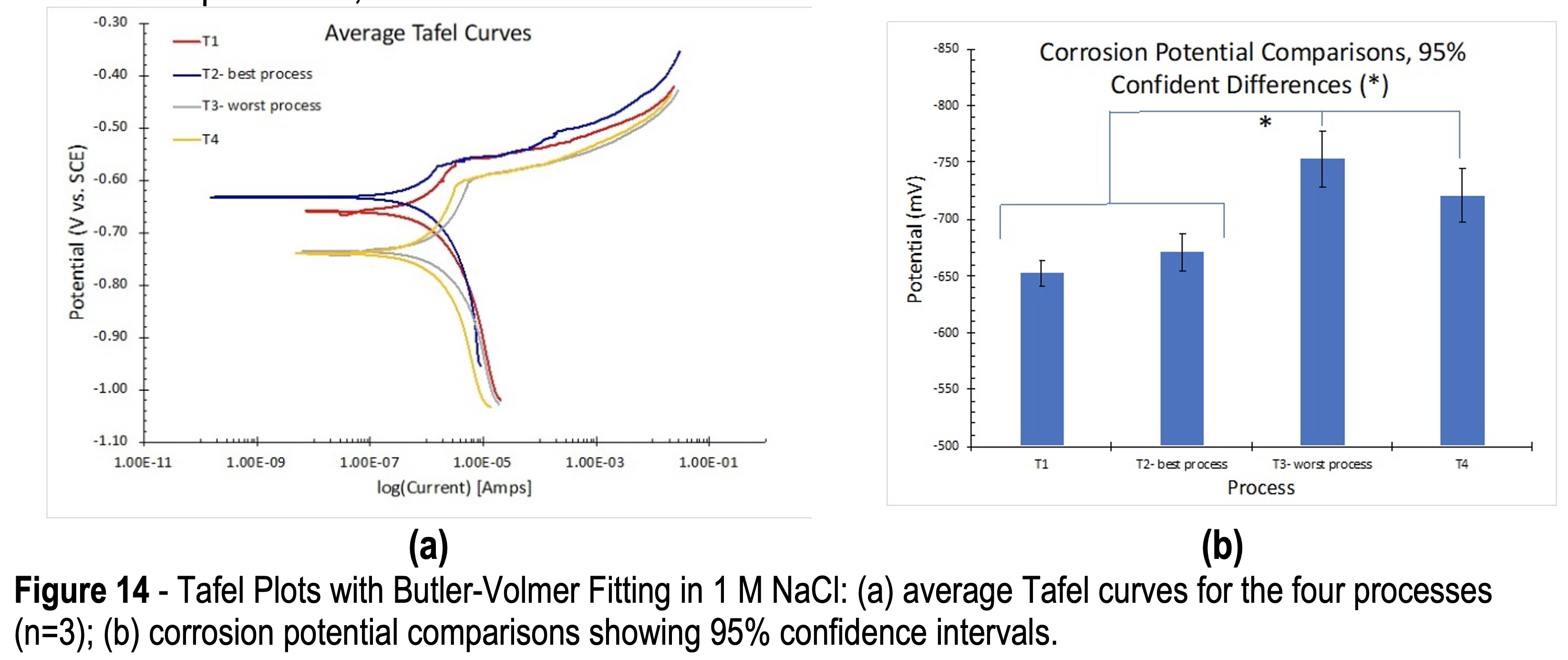
The Correlation Between Electrochemical Behavior and Neutral Salt Fog Corrosion on TCP Coated AA2024

Green nanomaterials and nanocomposites for corrosion inhibition applications

Full article: Inhibition effect of apium graveolens, punica