The MBOAT7-TMC4 Variant rs641738 Increases Risk of Nonalcoholic

Combined effects of the PNPLA3 rs738409, TM6SF2 rs58542926, and MBOAT7 rs641738 variants on NAFLD severity: a multicenter biopsy-based study1 - Journal of Lipid Research
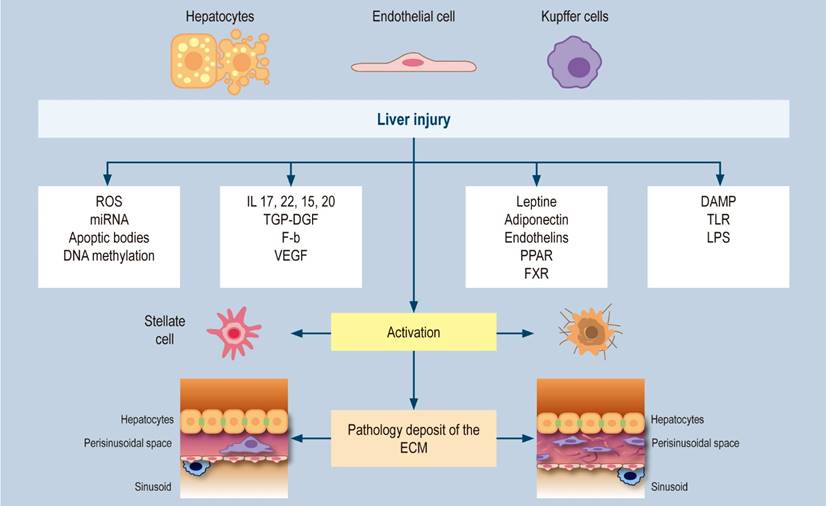
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease part 1: general aspects, epidemiology. pathophysiology and natural history

Noninvasive Evaluation of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease

Obesity-linked suppression of membrane-bound O-acyltransferase 7 (MBOAT7) drives non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
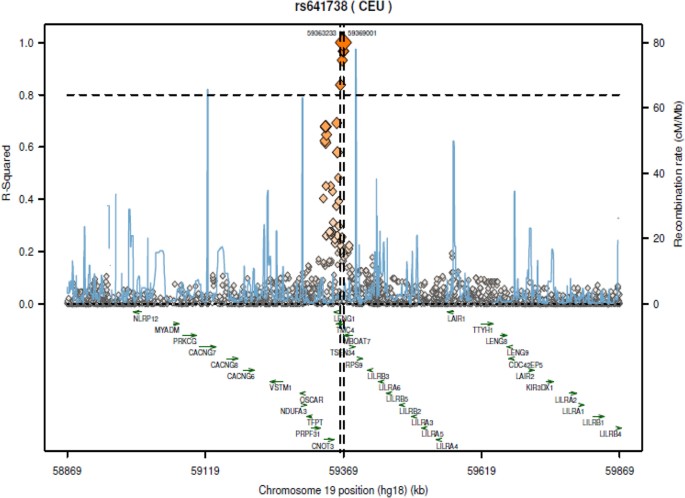
Lack of evidence supporting a role of TMC4-rs641738 missense variant—MBOAT7- intergenic downstream variant—in the Susceptibility to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
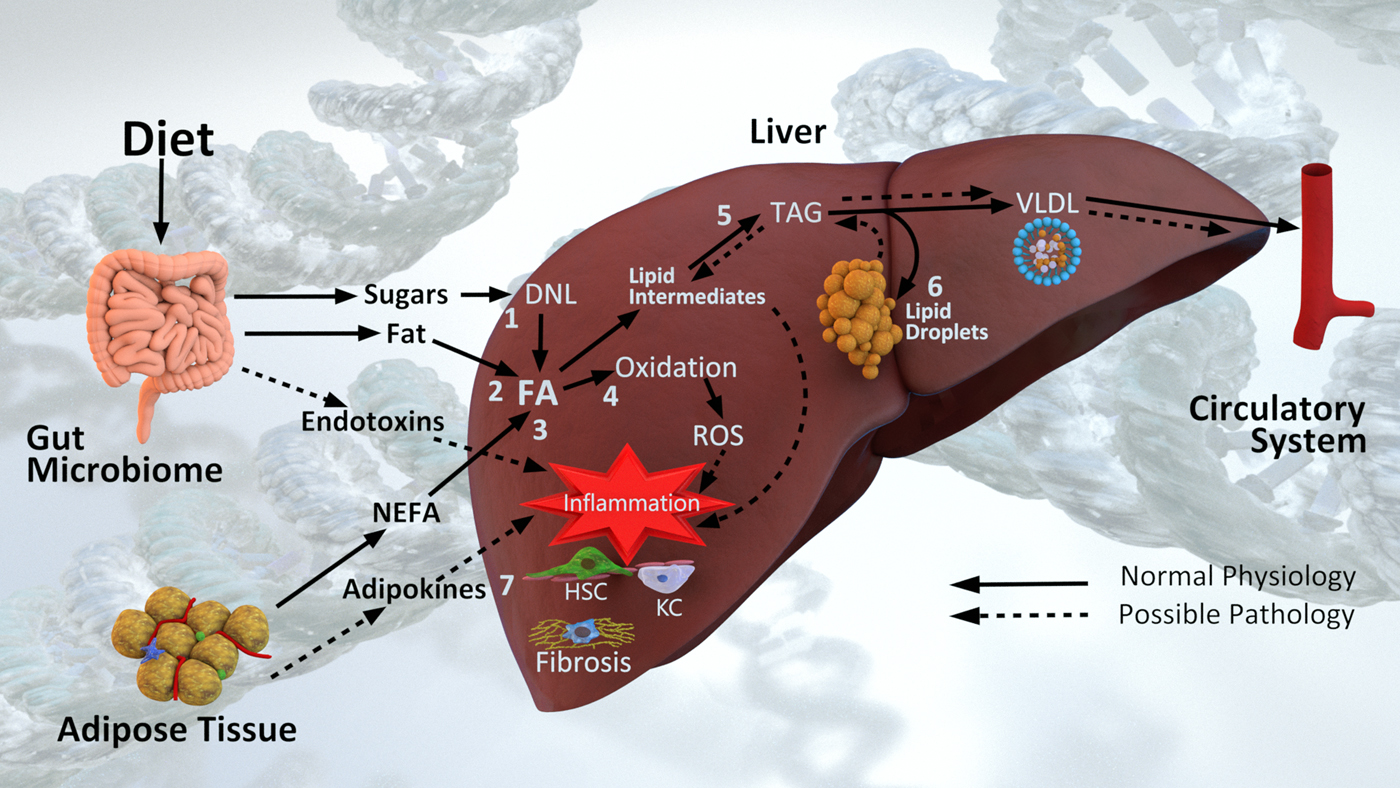
From sugar to liver fat and public health: systems biology driven studies in understanding non-alcoholic fatty liver disease pathogenesis, Proceedings of the Nutrition Society
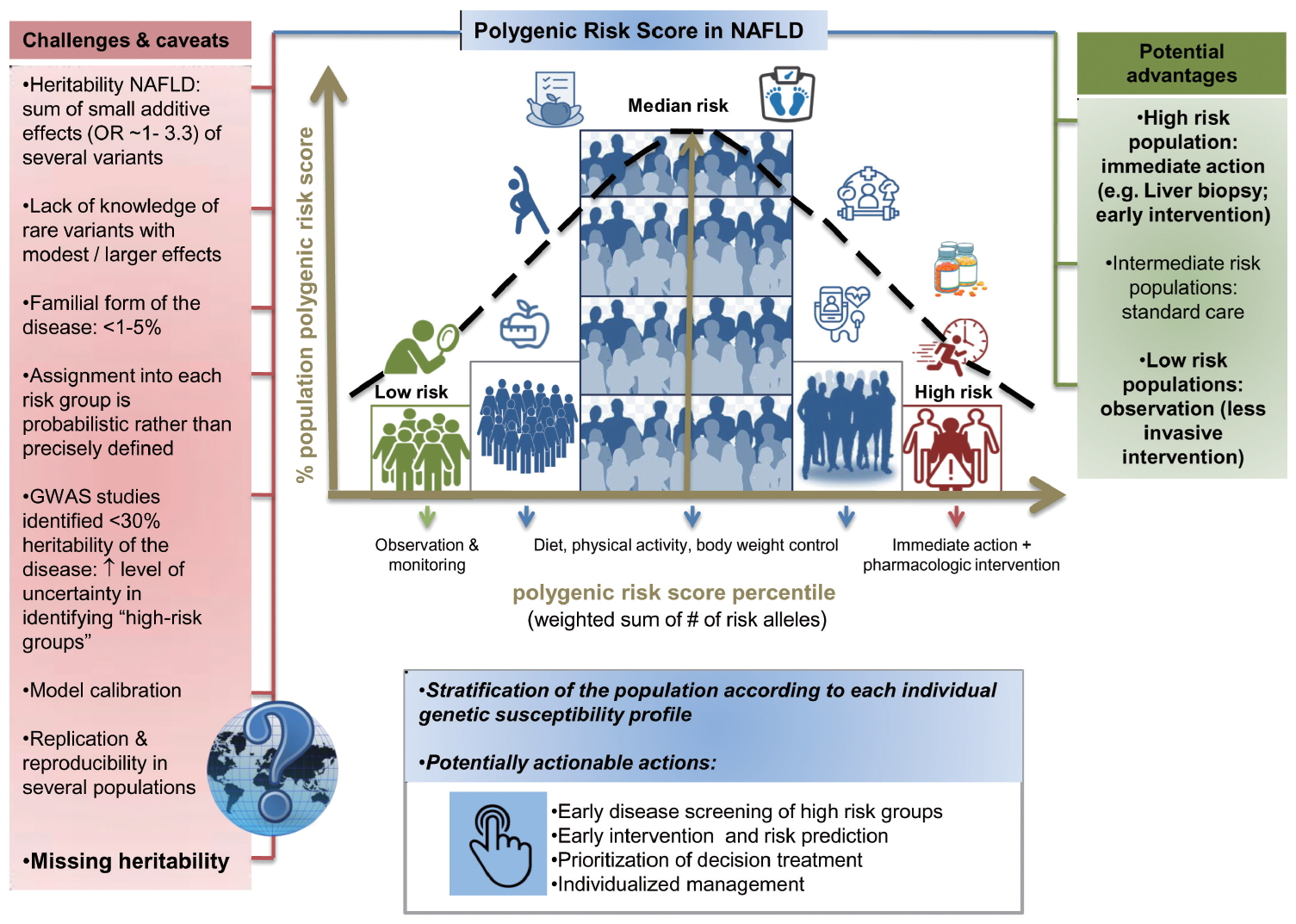
Precision medicine in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: New therapeutic insights from genetics and systems biology

Emerging risk factors for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease associated hepatocellular carcinoma

Investigating the Relationship Between Rare Genetic Variants and Fibrosis in Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease

Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
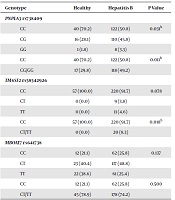
PNPLA3 and TM6SF2, but Not MBOAT7, Are Associated with Steatosis and HBV Viral Persistence in Pakistani Population, Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology

Distinct contributions of metabolic dysfunction and genetic risk factors in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Fatty Liver Research Group of the Korean Diabetes Association

PDF) Genetic risk factors associated with NAFLD Hepatoma Research and DongYun Kim
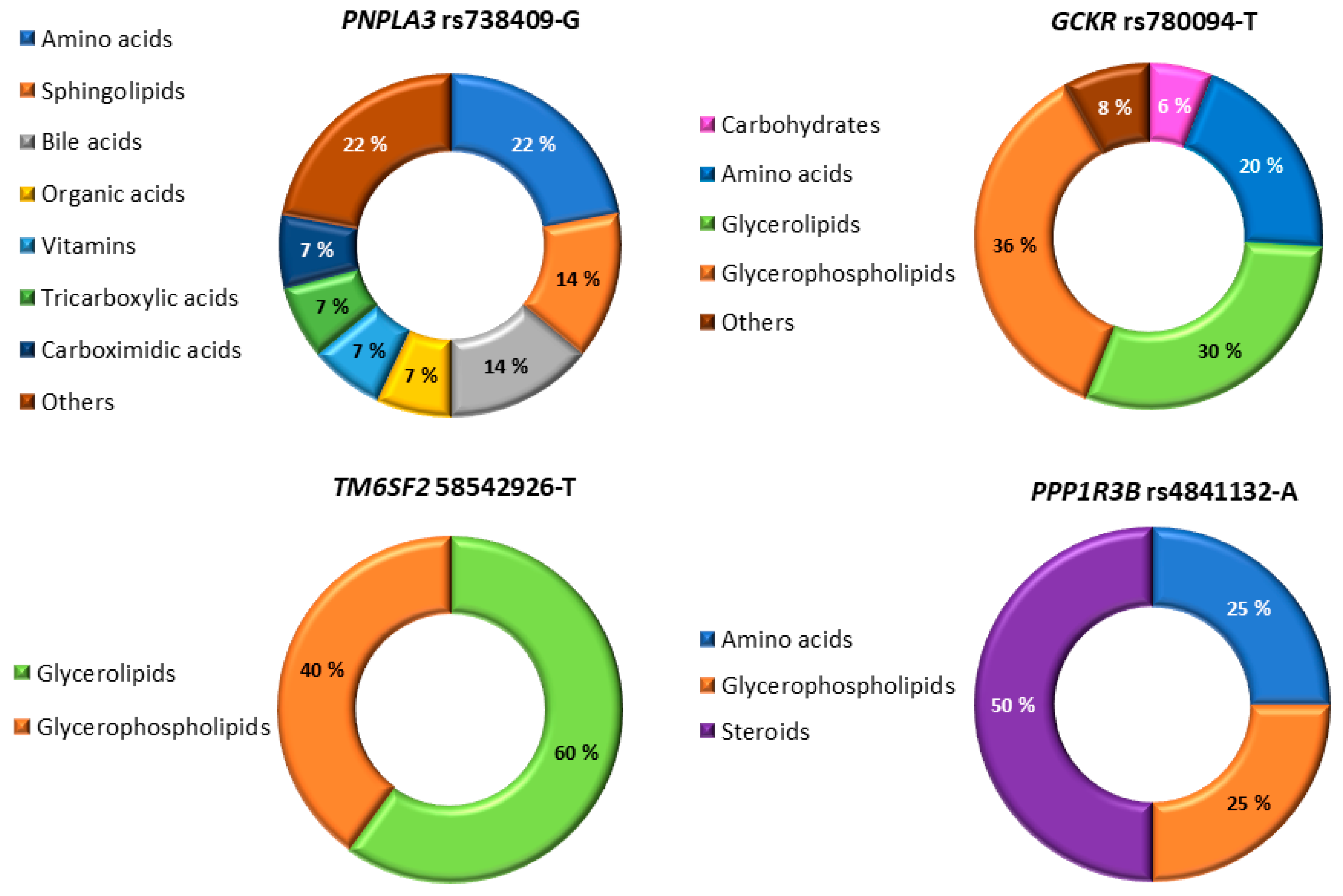
Metabolites, Free Full-Text









