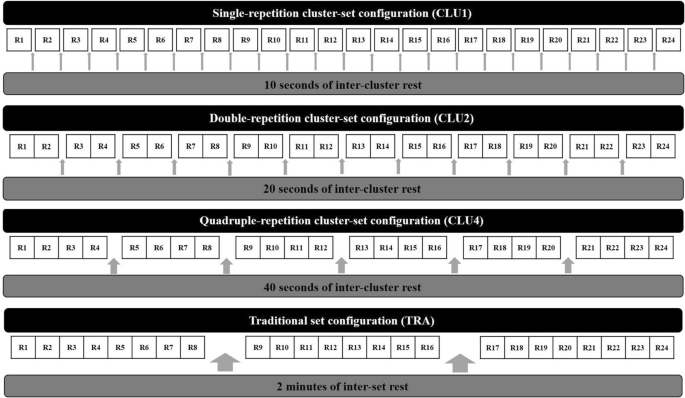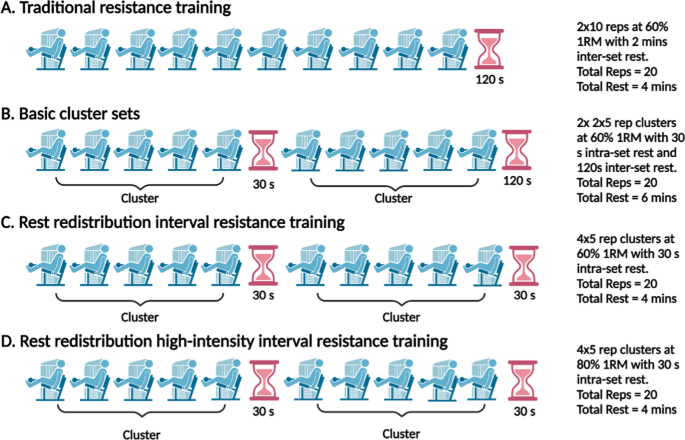
Cluster Sets to Prescribe Interval Resistance Training: A Potential Method to Optimise Resistance Training Safety, Feasibility and Efficacy in Cardiac Patients, Sports Medicine - Open
The integration of resistance training for cardiac patients leads to important health outcomes that are not optimally obtained with aerobic exercise; these include an increase in muscle mass, maintenance of bone mineral density, and improvements in muscular fitness parameters. Despite the proliferation of evidence supporting resistance exercise in recent decades, the implementation of resistance training is underutilised, and prescription is often sub-optimal in cardiac patients. This is frequently associated with safety concerns and inadequate methods of practical exercise prescription. This review discusses the potential application of cluster sets to prescribe interval resistance training in cardiac populations. The addition of planned, regular passive intra-set rest periods (cluster sets) in resistance training (i.e., interval resistance training) may be a practical solution for reducing the magnitude of haemodynamic responses observed with traditional resistance training. This interval resistance training approach may be a more suitable option for cardiac patients. Additionally, many cardiac patients present with impaired exercise tolerance; this model of interval resistance training may be a more suitable option to reduce fatigue, increase patient tolerance and enhance performance to these workloads. Practical strategies to implement interval resistance training for cardiac patients are also discussed. Preliminary evidence suggests that interval resistance training may lead to safer acute haemodynamic responses in cardiac patients. Future research is needed to determine the efficacy and feasibility of interval resistance training for health outcomes in this population.

PDF) Paired serum S-100B and neuron-specific enolase assay in early and fast assessment of brain damage after cardiac arrest
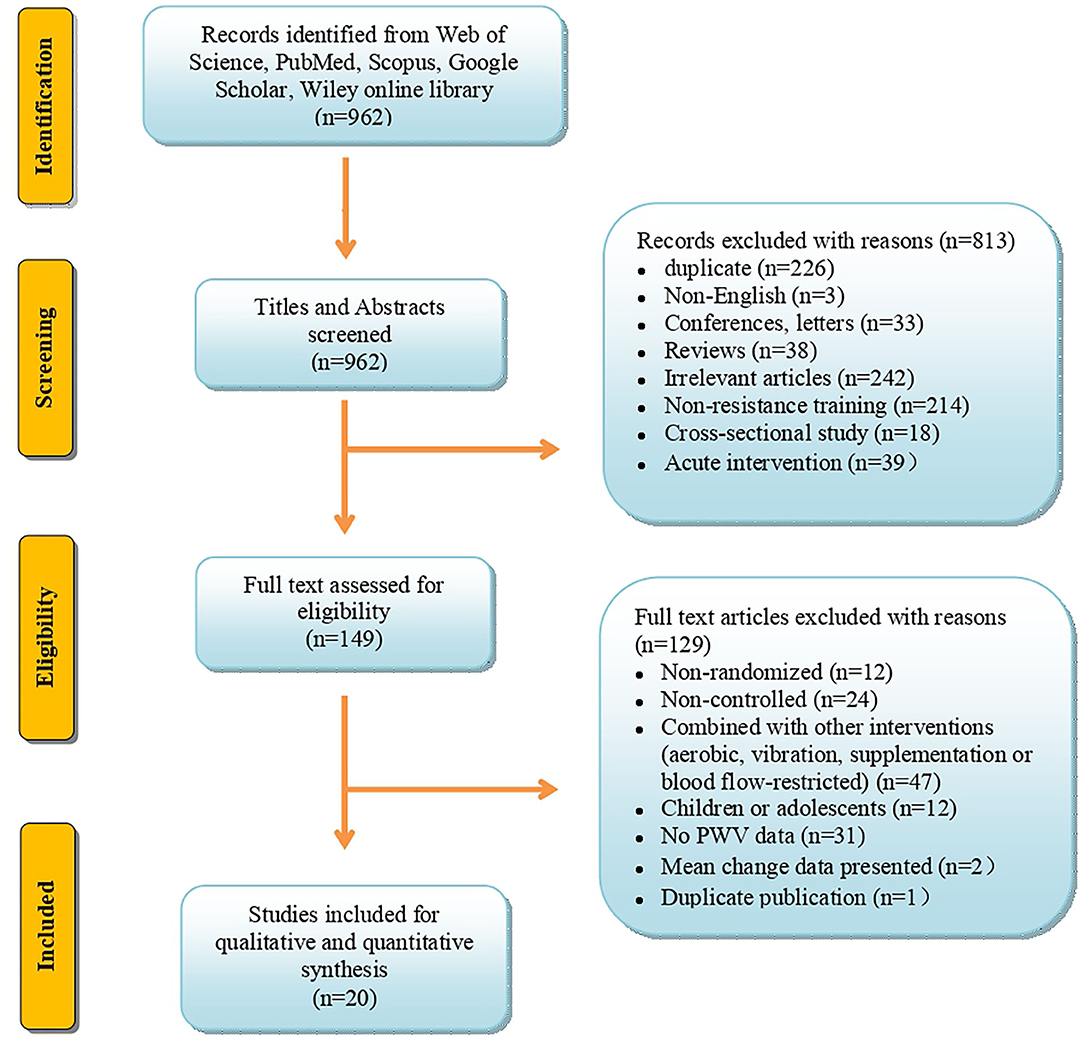
Frontiers Low-to-Moderate-Intensity Resistance Exercise Effectively Improves Arterial Stiffness in Adults: Evidence From Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression Analysis
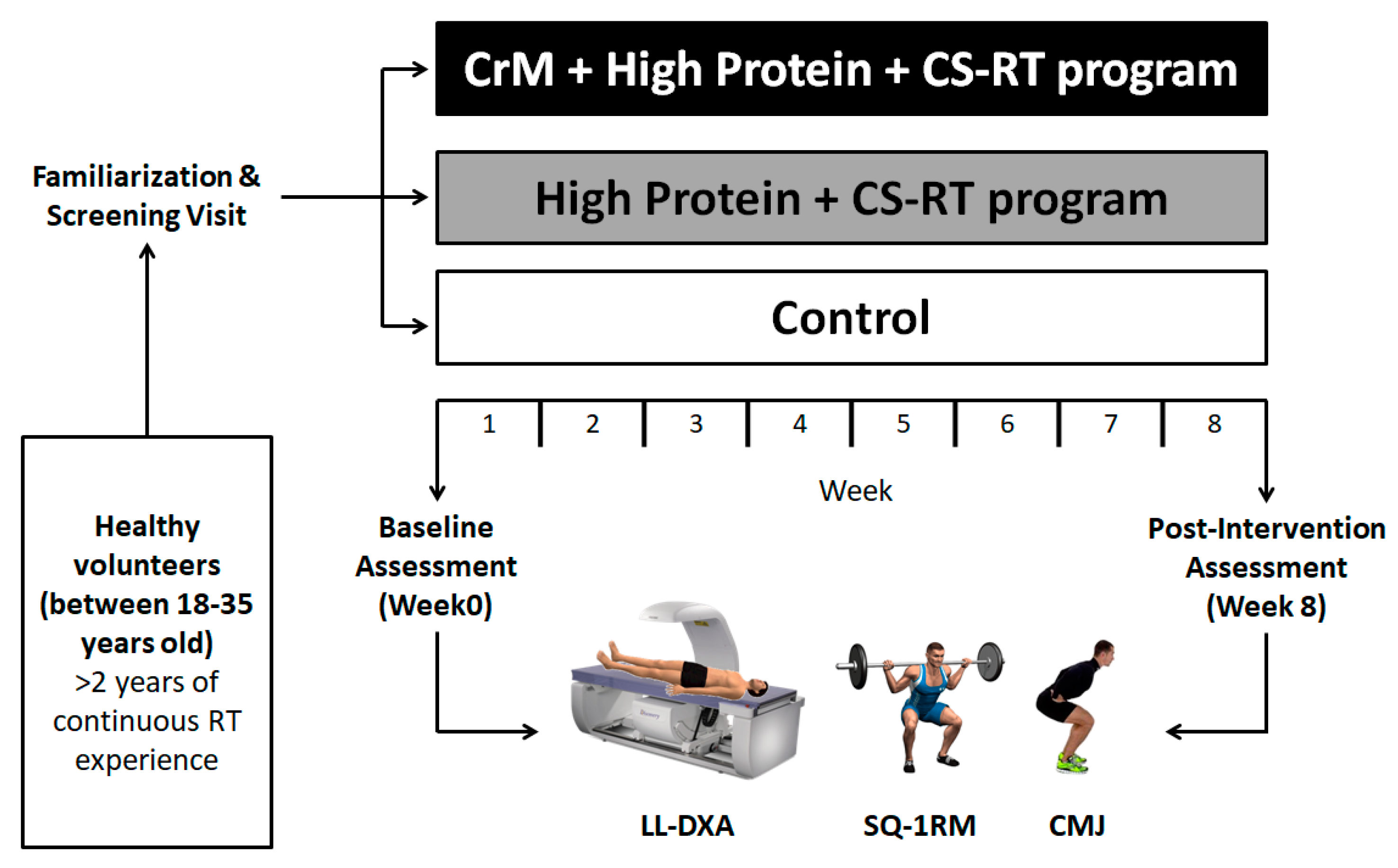
Nutrients, Free Full-Text

Newsletter September 2023
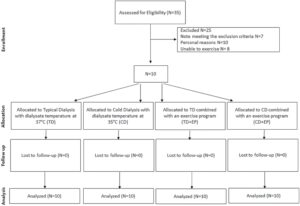
/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/The-Acut

High-intensity interval training: a review of its impact on glucose control and cardiometabolic health

The Role of Exercise in Diabetes - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf
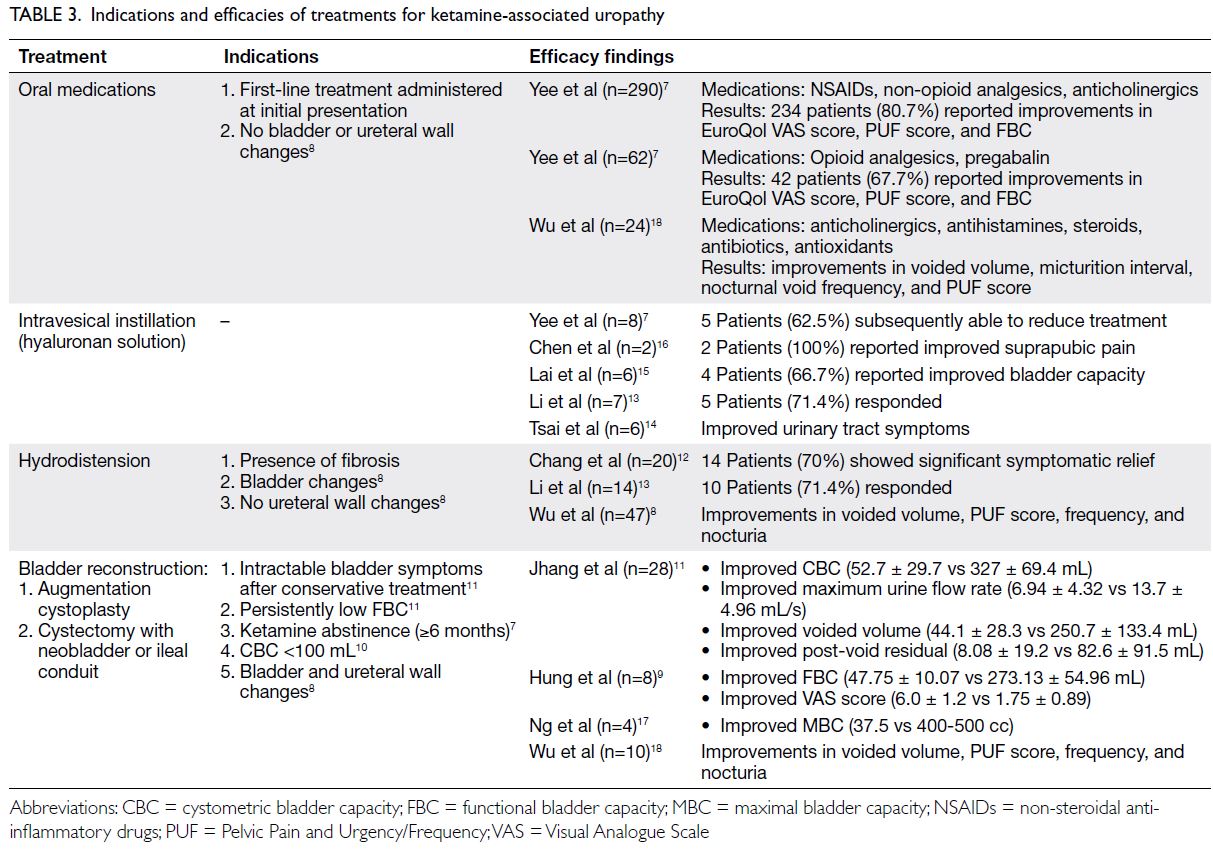
Review Article

📣 New publication: Cluster Sets to Prescribe Interval Resistance Training 🏋️♀️, Kim Way posted on the topic
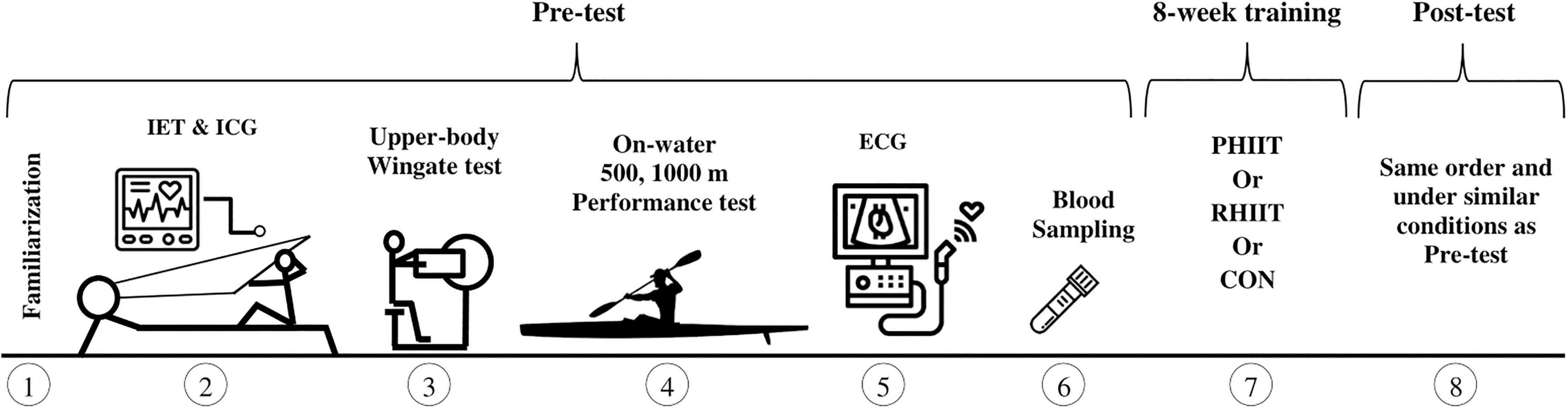
Frontiers Effects of a New Form of Resistance-Type High-Intensity Interval Training on Cardiac Structure, Hemodynamics, and Physiological and Performance Adaptations in Well-Trained Kayak Sprint Athletes
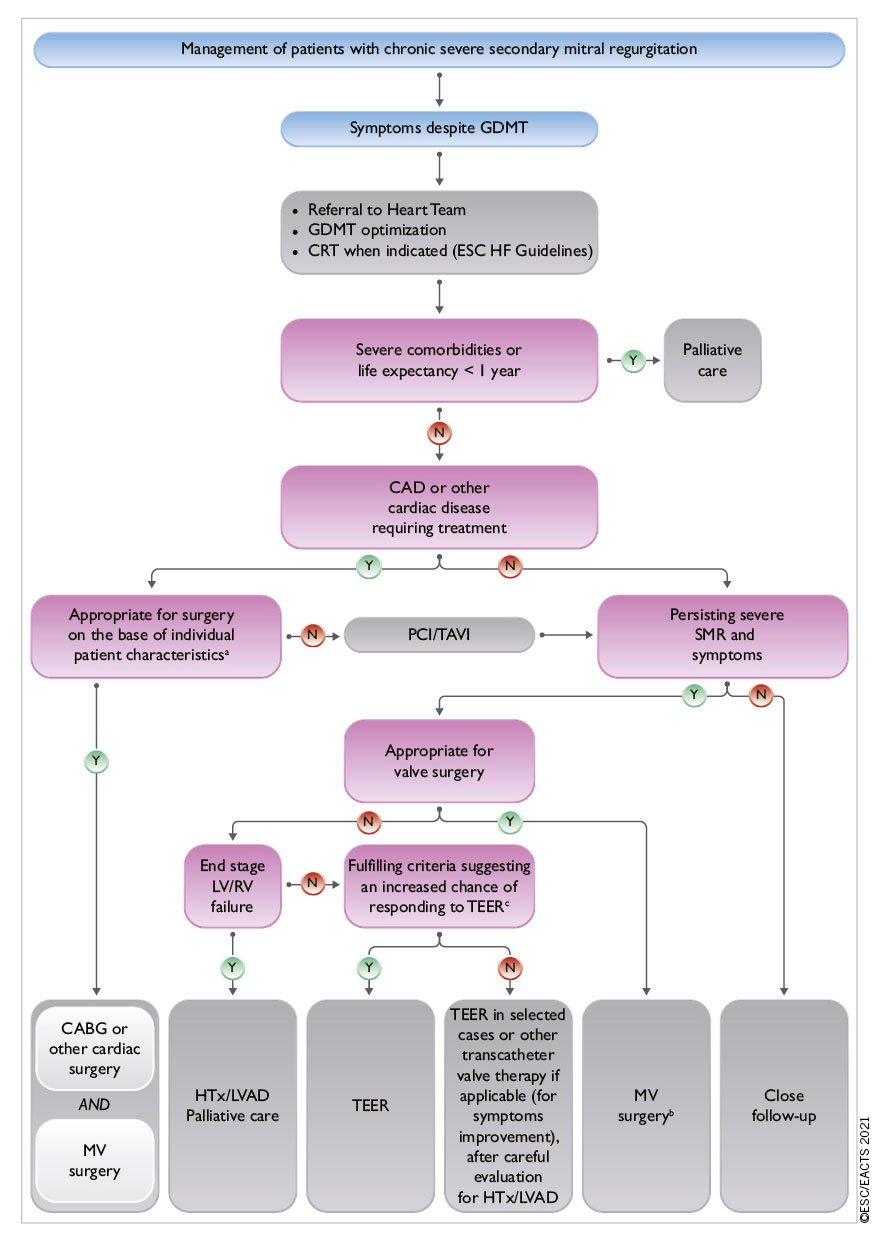
2021 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease

PDF] Dynamic strength training intensity in cardiovascular rehabilitation: is it time to reconsider clinical practice? A systematic review
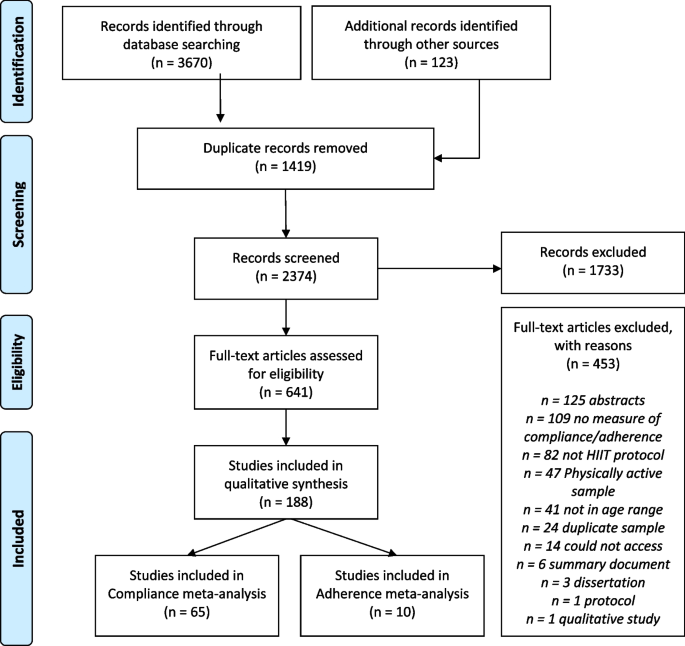
Rates of compliance and adherence to high-intensity interval training: a systematic review and Meta-analyses, International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity