Mean width (a), depth (b), and velocity (c) at lower and upper reaches
Download scientific diagram | Mean width (a), depth (b), and velocity (c) at lower and upper reaches in each season. Error bars are one standard error. Data from fall were excluded due to dry conditions at the upper reach. An asterisk next to the season designates a significant difference (α = 0.05) between reaches within that season. from publication: Influence of a Spring on Fish Communities and Habitat in an Ozark Stream | Springs influence water temperature and flow of streams; however, little information exists on the effects of springs on fish communities and their potential as refugia. This study examined the impacts of a spring on a wadeable stream. Fish, water quality, and physical | Fishing Communities, Streams and Upstream | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Projectile Motion

Stratification (water) - Wikipedia

Species richness (a) and number of intolerant species (b) for lower and
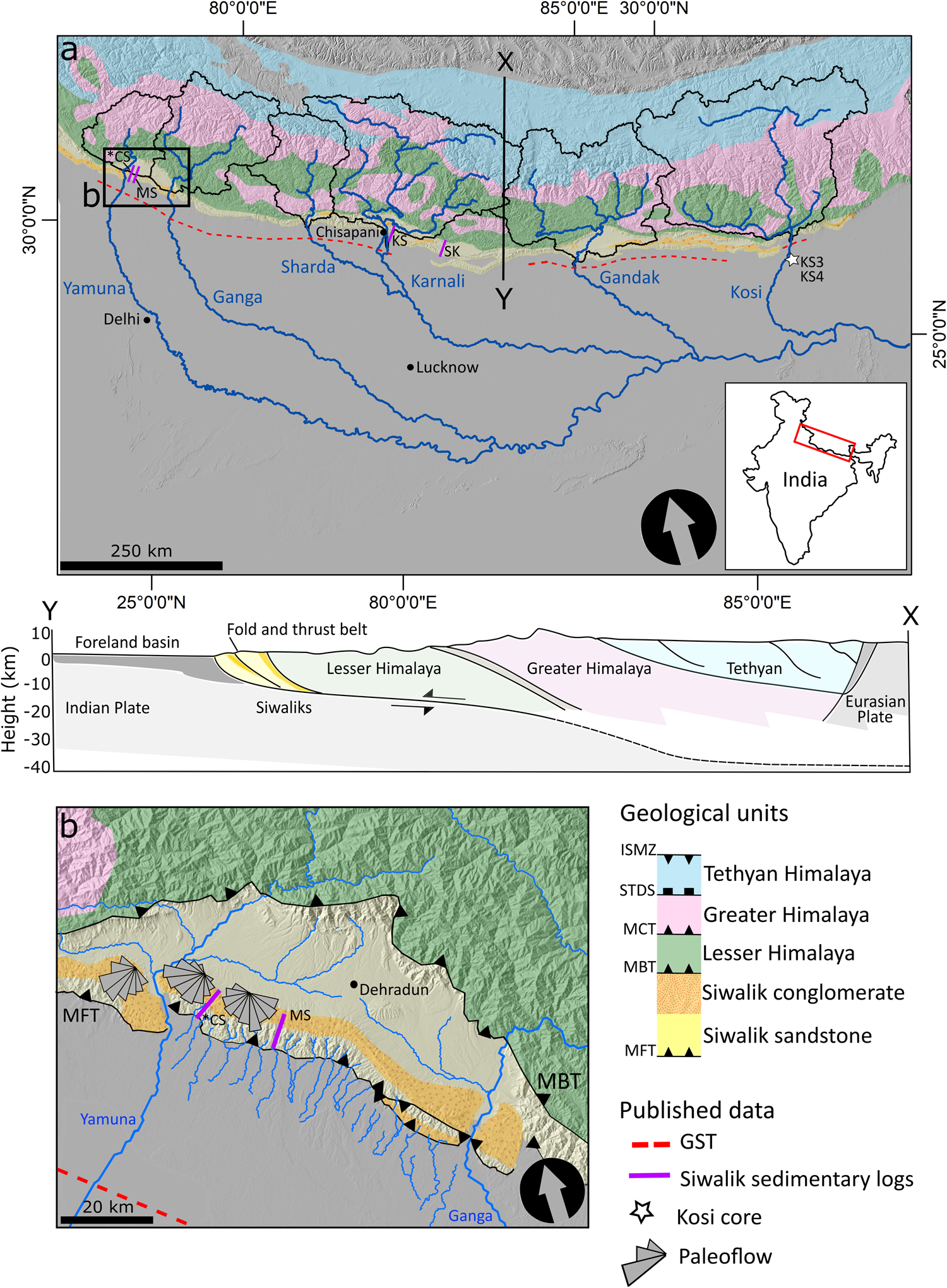
Hyperconcentrated floods cause extreme gravel transport through the sandy rivers of the Gangetic Plains
Atmospheric circulation - Wikipedia

Hybrid quantum systems with high-T $$_c$$ superconducting resonators
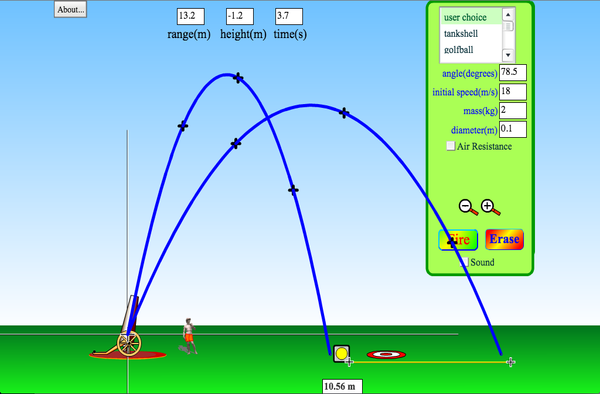
Projectile Motion

Flow Rate and Its Relation to Velocity

How do seismologists locate an earthquake?

Investigation on ultrasonic-assisted grinding of characteristics of C/SiC composites by brazed and electroplated diamond wheels
Vernier Calliper: Definition, Diagram, Least Count, Parts & Applications

Door – Minecraft Wiki

Mean water temperature (a), dissolved oxygen (b), and pH (c) at lower

PDF) Influence of a Spring on Fish Communities and Habitat in an Ozark Stream

Number of respondents for each scenario