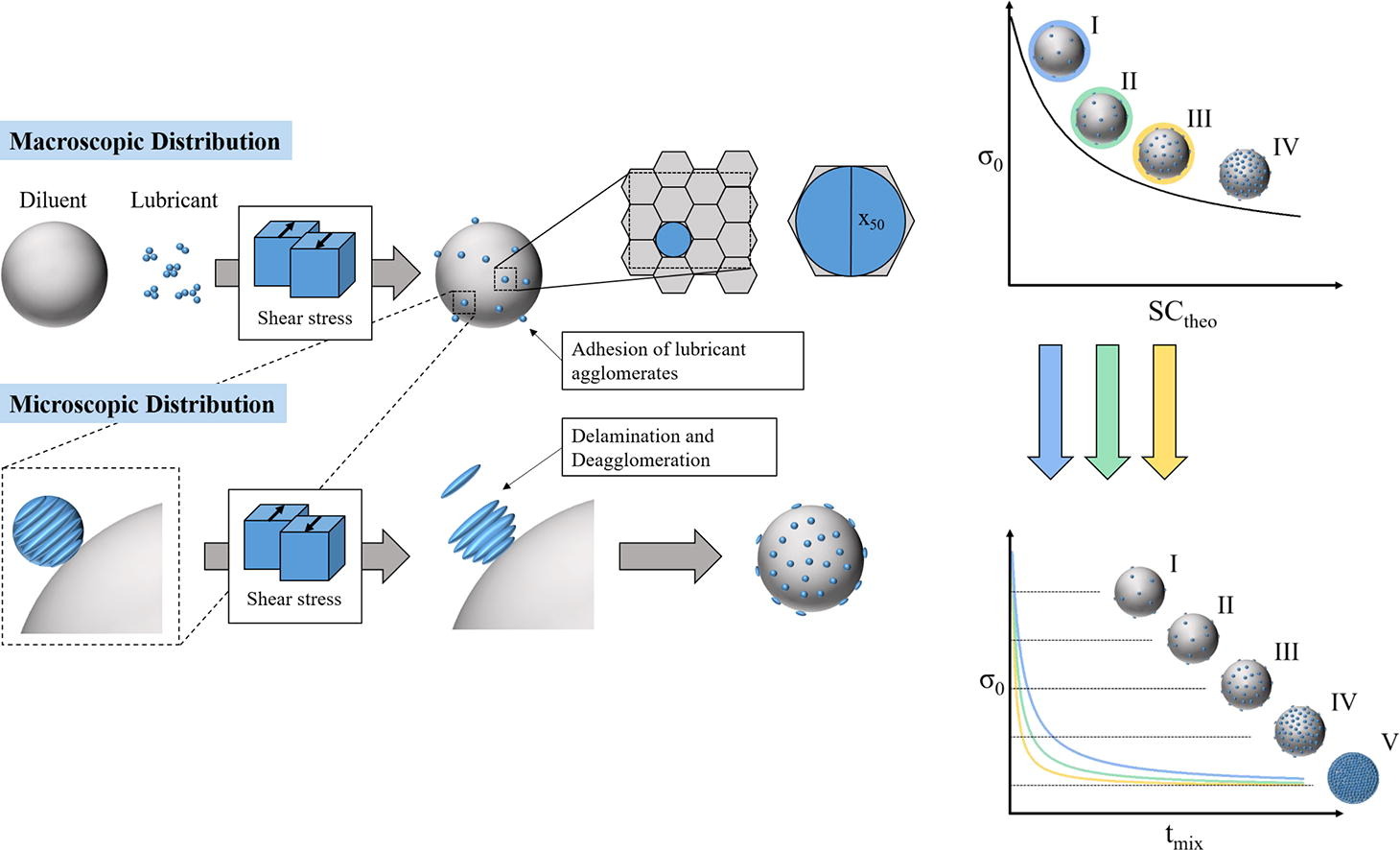
Effect of particle size on the dispersion behavior of magnesium stearate blended with microcrystalline cellulose - Pharma Excipients
The impact of lubricant concentration and mixing time on tensile strength of tablets consisting of MCC and magnesium stearate was evaluated
The majority of tablets manufactured contain lubricants to reduce friction during ejection. However, especially for plastically deforming materials, e.g., microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), the internal addition of lubricants is known to reduce tablet

Effect of sieve fractions in pressed tablet on dissolution rate and

PharmaExcipients.com on LinkedIn: Electrospinning of pullulan-based orodispersible films containing…

Microneedles: How they are used for transdermal drug delivery, PharmaExcipients.com posted on the topic

Microcrystalline Cellulose as Pharmaceutical Excipient

PharmaExcipients.com on LinkedIn: Application of Design of Experiment in the Optimization of Apixaban-Loaded…

PDF) Impact of Magnesium Stearate Presence and Variability on Drug Apparent Solubility Based on Drug Physicochemical Properties

Materials, Free Full-Text

Effect of magnesium stearate solid lipid nanoparticles as a lubricant on the properties of tablets by direct compression - ScienceDirect

PharmaExcipients.com on LinkedIn: Chitosan/Solid-Lipid Nanoparticles Hybrid Gels for Vaginal Delivery of…

Prasad Panzade, Ph.D. on LinkedIn: SmartEx® Plus: a New Co-Processed Excipient for Oral Disintegration…

Investigation of Dispersion Kinetics of Particulate Lubricants and their Effect on the Mechanical Strength of MCC Tablets

Prasad Panzade, Ph.D. on LinkedIn: Hot melt extrusion for enhanced dissolution and intestinal absorption of…

PharmaExcipients.com on LinkedIn: ApoE - functionalization of nanoparticles for targeted brain delivery - a…

PharmaExcipients.com on LinkedIn: Modern Nanocarriers as a Factor in Increasing the Bioavailability and…