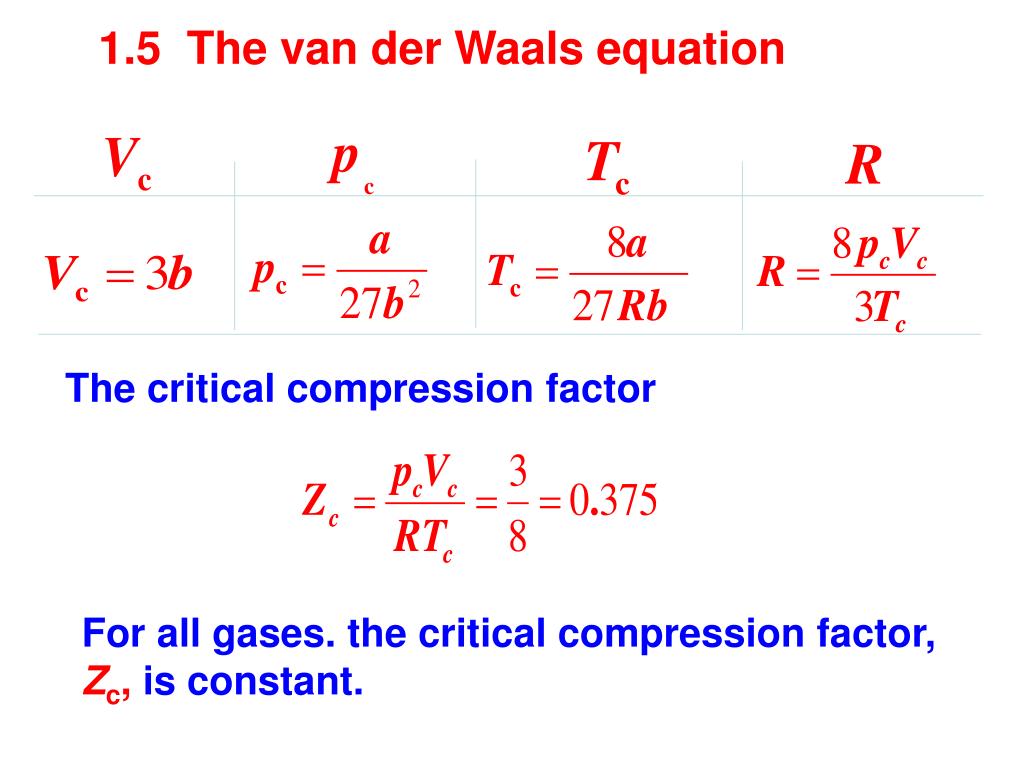
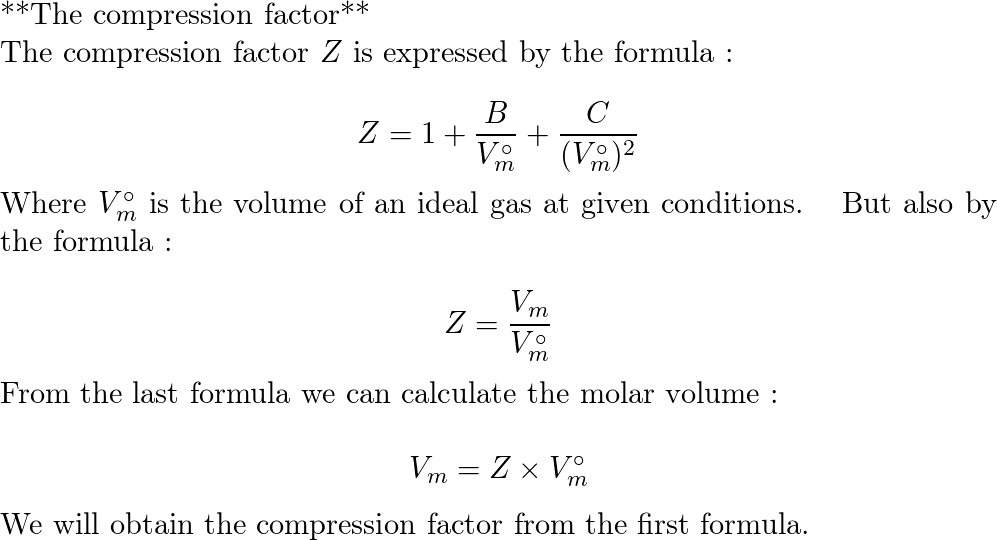The compression factor (compressibility factor) for 1 mol of a van der
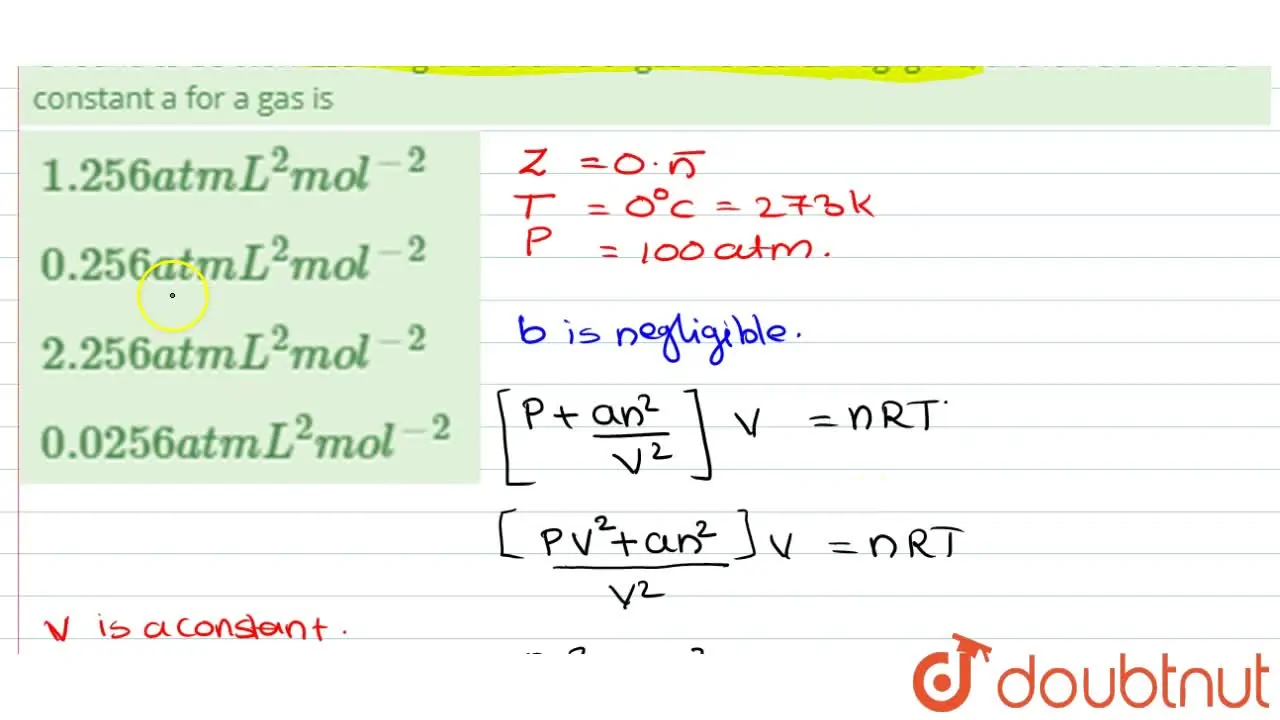
For 1 mol of a gas, the van der Waals equation is (P+(a)/(V(m)^(2)))(V(m)-b)=RT Ignoring b, we get (given volume of gas molecule is negligible) (P+(a)/(V(m)^(2)))V(m)=RT ltbgt or pV(m)+(a)/(V(m))=RT or (pV(m))/(RT)+(a)/(V(m)RT)=1 or Z=(pV(m))/(RT)=1-(a)/(V(m)RT) (i) It is given that Z=(pV(m))/(RT)=0.5implies V(m)=(0.5RT)/(P) With this, equation (i) becomes 0.5=1-(a)/((0.5RT//p)RT) or a=(0.5)((0.5RT)/(p))RT=0.25(R^(2)T^(2))/(p) Substiuting the given values, we get a=(0.25)[((0.082L atm K^(-1)mol^(-1))^(2)(273 K)^(2))/((100 atm))] =1.2528 L^(2) atm mol^(-2)

is characterised by van der Waals coefficients that are dependent on t

Only a small number of molecules have very high velocity.

Malayalam] The Compressibility factor for one mole of a van der Waal
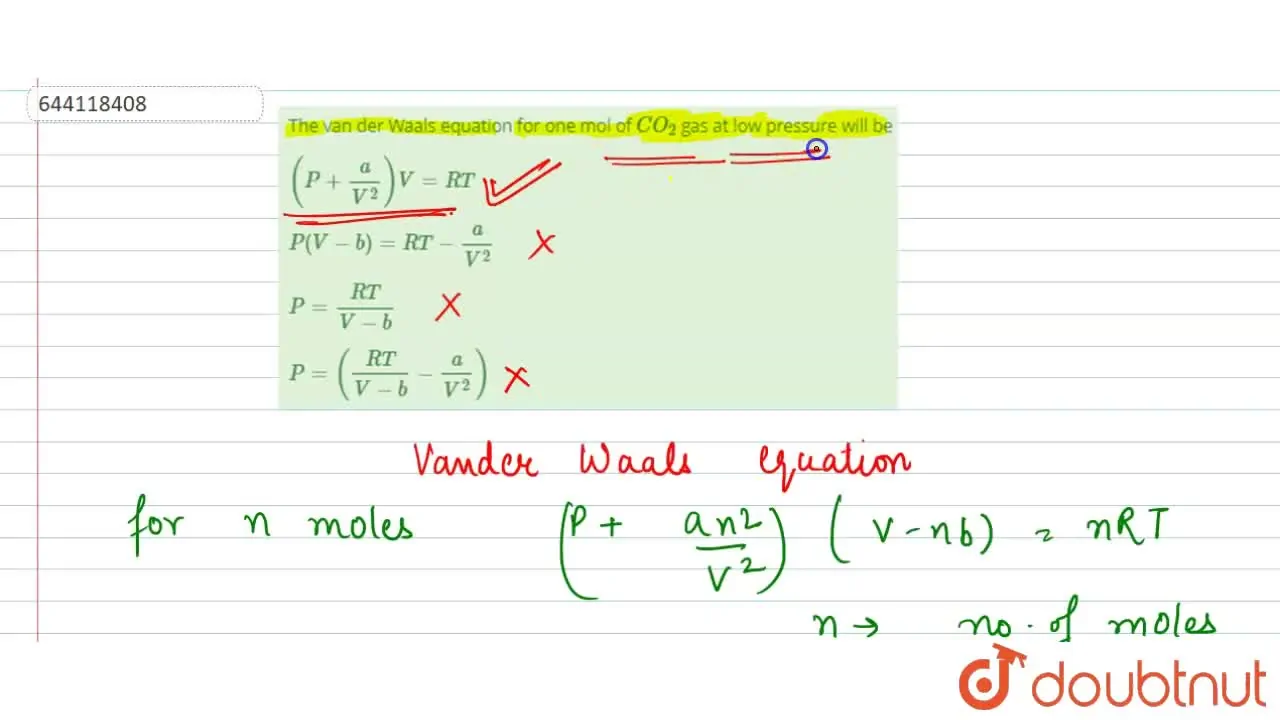
The van der Waals equation for one mol of CO(2) gas at low pressure wi
One mole of a monoatomic real gas satisfies the equation p(V-b)=RT wh

To an evacuated vessel with movable piston under external pressure of
Malayalam] The compressibility factor for definite amount of van der

Bengali] The compressibility factor (Z) of one mole of a van der Waal

The compression factor (compressibility factor) for 1 mol of a van der

Match the entries in column I with entries in Column II and then pick

A mixture of ethane (C(2)H(6)) and ethene (C(2)H(4)) occupies 40 L at