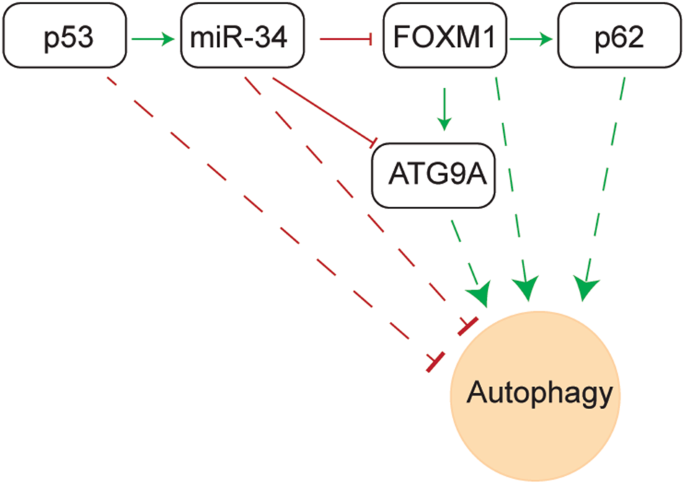
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated inactivation of miR-34a and miR-34b/c in HCT116 colorectal cancer cells: comprehensive characterization after exposure to 5-FU reveals EMT and autophagy as key processes regulated by miR-34

MicroRNA-34 family: a potential tumor suppressor and therapeutic candidate in cancer, Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research
The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis

Rfp Gfp Lc3 Plasmid (Addgene inc), Bioz
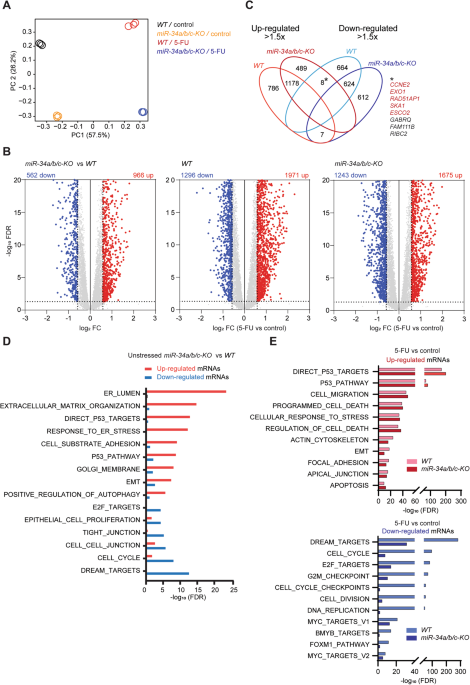
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated inactivation of miR-34a and miR-34b/c in HCT116 colorectal cancer cells: comprehensive characterization after exposure to 5-FU reveals EMT and autophagy as key processes regulated by miR-34

PDF] The Critical Role of Dysregulated FOXM1–PLAUR Signaling in Human Colon Cancer Progression and Metastasis

Genetic determinants of FOXM1 overexpression in epithelial ovarian
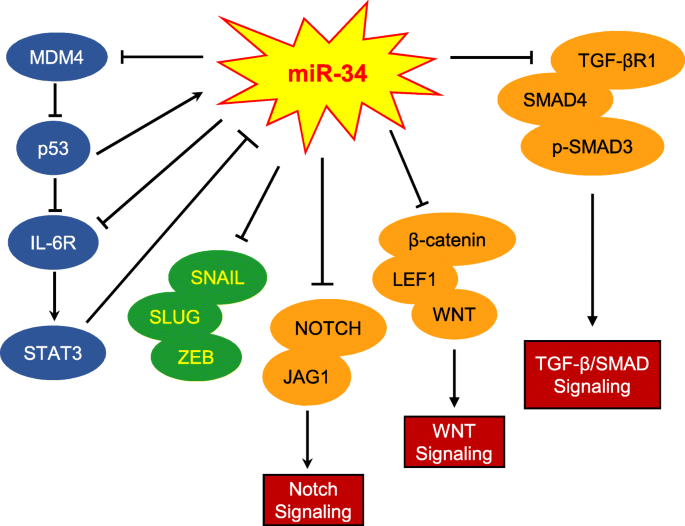
MicroRNA-34 family: a potential tumor suppressor and therapeutic candidate in cancer, Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research
Addgene: pMRX-IP-GFP-LC3-RFP Citations

c-Kit is repressed after ectopic p53 and miR-34a expression in

miR-34a inhibits basal and SCF-induced migration and invasion of

Salicylate induces AMPK and inhibits c-MYC to activate a NRF2/ARE/miR-34a/b/ c cascade resulting in suppression of colorectal cancer metastasis

The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis

Distribution of patients' characteristics and prognosis analysis

Structure, lipid scrambling activity and role in autophagosome

Restoring microRNA-34a overcomes acquired drug resistance and disease progression in human breast cancer cell lines via suppressing the ABCC1 gene







