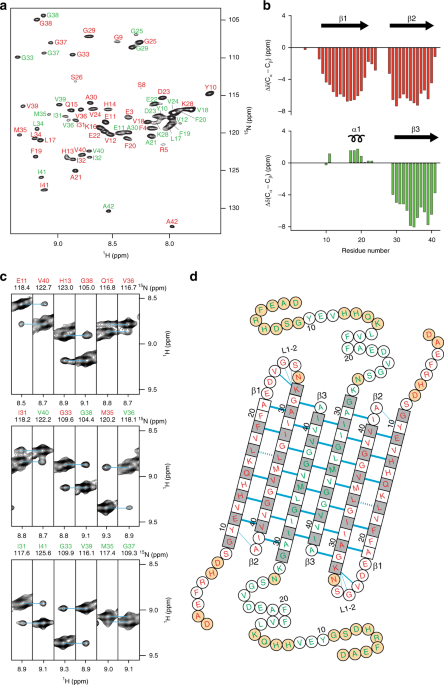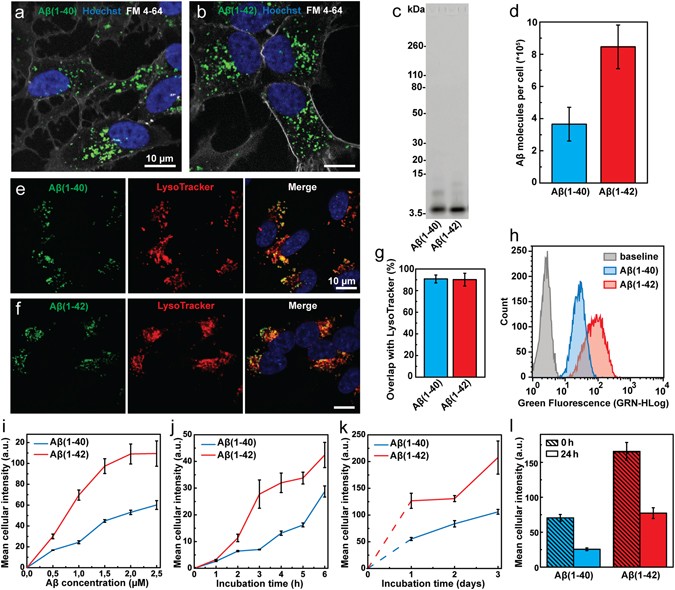
Endocytic uptake of monomeric amyloid-β peptides is clathrin- and dynamin-independent and results in selective accumulation of Aβ(1–42) compared to Aβ(1–40)

Towards the integrative theory of Alzheimer's disease: linking molecular mechanisms of neurotoxicity, beta-amyloid biomarkers, and the diagnosis

Amyloid-beta peptides 40 and 42 employ distinct molecular pathways for cell entry and intracellular transit at the BBB endothelium

Uptake of Aβ by OATPs might be a new pathophysiological mechanism of Alzheimer disease, BMC Neuroscience

IJMS, Free Full-Text

Uptake of Aβ(1-40), Aβ(1-42) and Trf in SH-SY5Y cells under conditions

Clathrin-independent endocytosis: an increasing degree of complexity

Evidence for aggregation-independent, PrPC-mediated Aβ cellular internalization. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Amyloid-beta peptides 40 and 42 employ distinct molecular pathways for cell entry and intracellular transit at the BBB endothelium

Designed Cell-Penetrating Peptide Inhibitors of Amyloid-beta Aggregation and Cytotoxicity - ScienceDirect

Misfolded amyloid-β-42 impairs the endosomal–lysosomal pathway

Alzheimer's disease linked Aβ42 exerts product feedback inhibition on γ-secretase impairing downstream cell signaling

Endocytosis in β-amyloid biology and Alzheimer's disease - ScienceDirect