Medication induced fetal bladder rupture: a case report
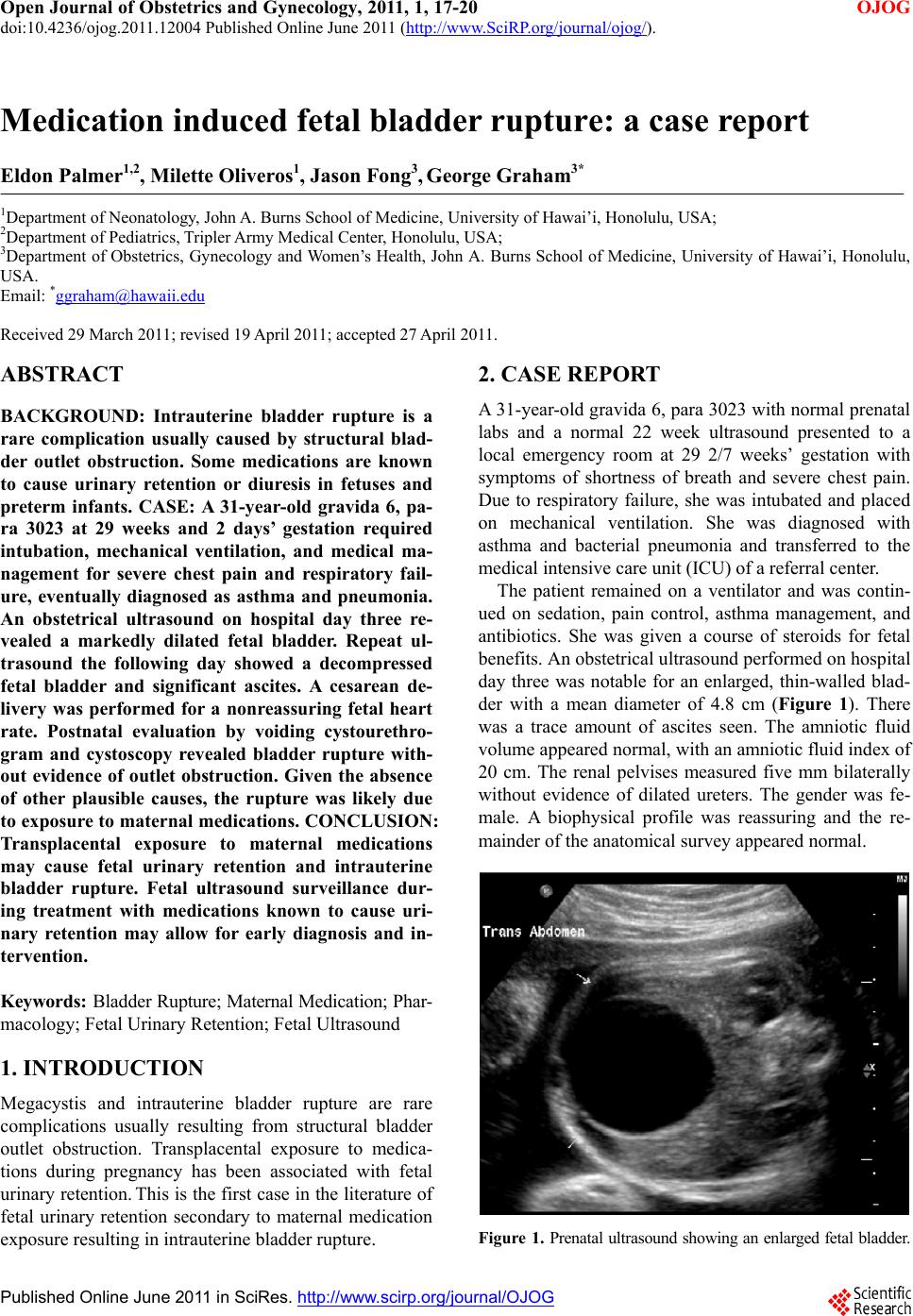
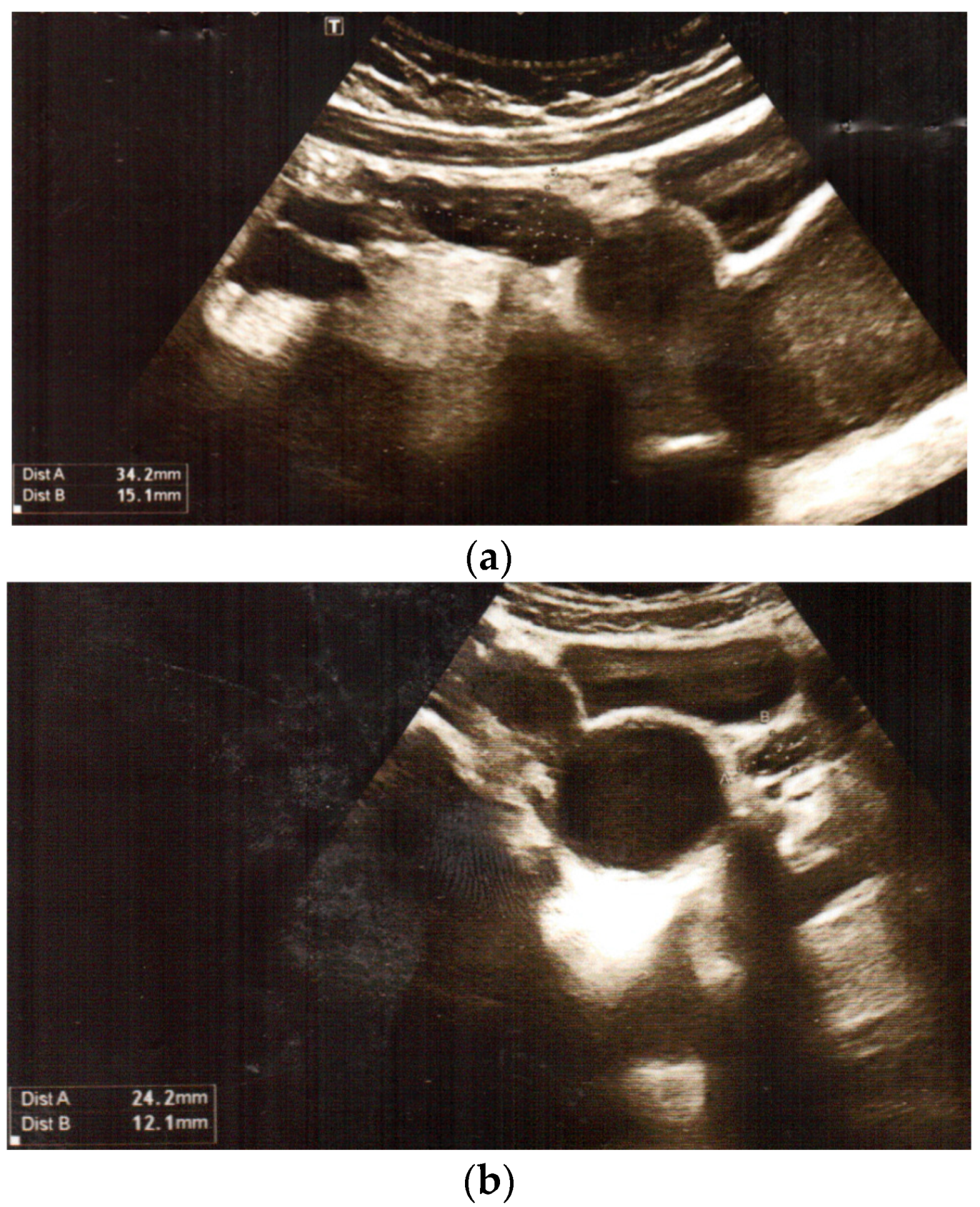
BACKGROUND: Intrauterine bladder rupture is a rare complication usually caused by structural bladder outlet obstruction. Some medications are known to cause urinary retention or diuresis in fetuses and preterm infants. CASE: A 31-year-old gravida 6, para 3023 at 29 weeks and 2 days’ gestation required intubation, mechanical ventilation, and medical management for severe chest pain and respiratory failure, eventually diagnosed as asthma and pneumonia. An obstetrical ultrasound on hospital day three revealed a markedly dilated fetal bladder. Repeat ultrasound the following day showed a decompressed fetal bladder and significant ascites. A cesarean delivery was performed for a nonreassuring fetal heart rate. Postnatal evaluation by voiding cystourethrogram and cystoscopy revealed bladder rupture without evidence of outlet obstruction. Given the absence of other plausible causes, the rupture was likely due to exposure to maternal medications. CONCLUSION: Transplacental exposure to maternal medications may cause fetal urinary retention and intrauterine bladder rupture. Fetal ultrasound surveillance during treatment with medications known to cause urinary retention may allow for early diagnosis and intervention.

Medication induced fetal bladder rupture: a case report
JCM, Free Full-Text

Unusual fetal ascites and spontaneous bladder rupture in a female fetus: a case report, Journal of Medical Case Reports

Uterine rupture in the first trimester: a case report and review of the literature, Journal of Medical Case Reports

Antepartum fetal bladder rupture leading to urinary ascitis

PDF) Medication induced fetal bladder rupture: a case report

Ultrasound image of fetal bladder obstruction with the characteristic

Case Study Report on PIH and Severe Pre eclampsia

Perinephric urinoma following spontaneous renal rupture in the third trimester of pregnancy: a case report and brief review of the literature, BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth
Trans-abdominal in vivo placental vessel occlusion using High Intensity Focused Ultrasound

Organ-preserving treatment of an epididymal abscess in a patient with spinal cord injury

Urinary effects of morphine in preterm infants

Fetal megacystis, Radiology Reference Article
Type II Residual Horn Uterine Pregnancy Complicated with Unilateral Kidney Deficiency: A Case Report









