Heat shock increases levels of reactive oxygen species, autophagy
Hyperthermia is a promising anticancer treatment used in combination with radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Temperatures above 41.5 °C are cytotoxic and …
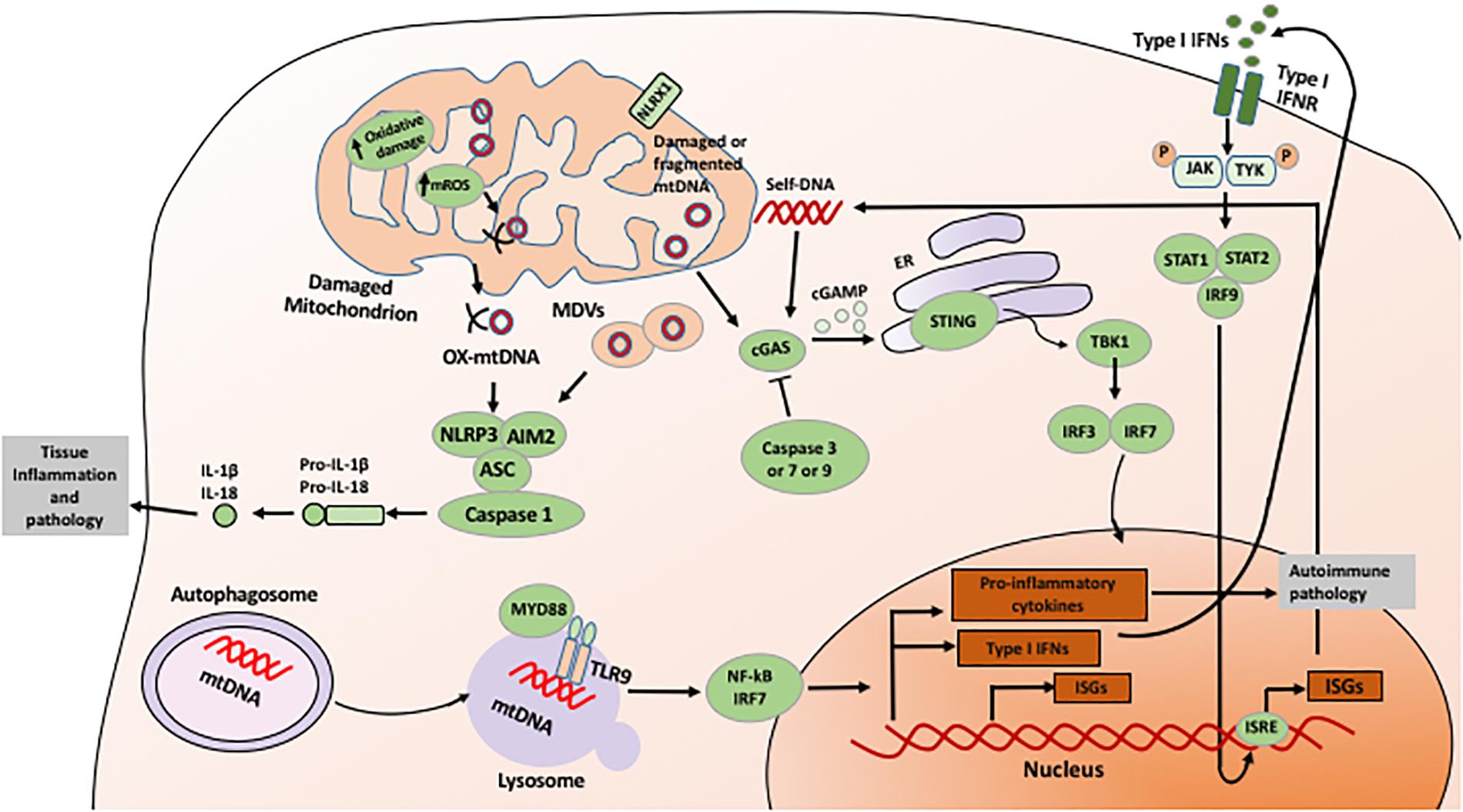
Frontiers Mitochondria, Oxidative Stress and Innate Immunity
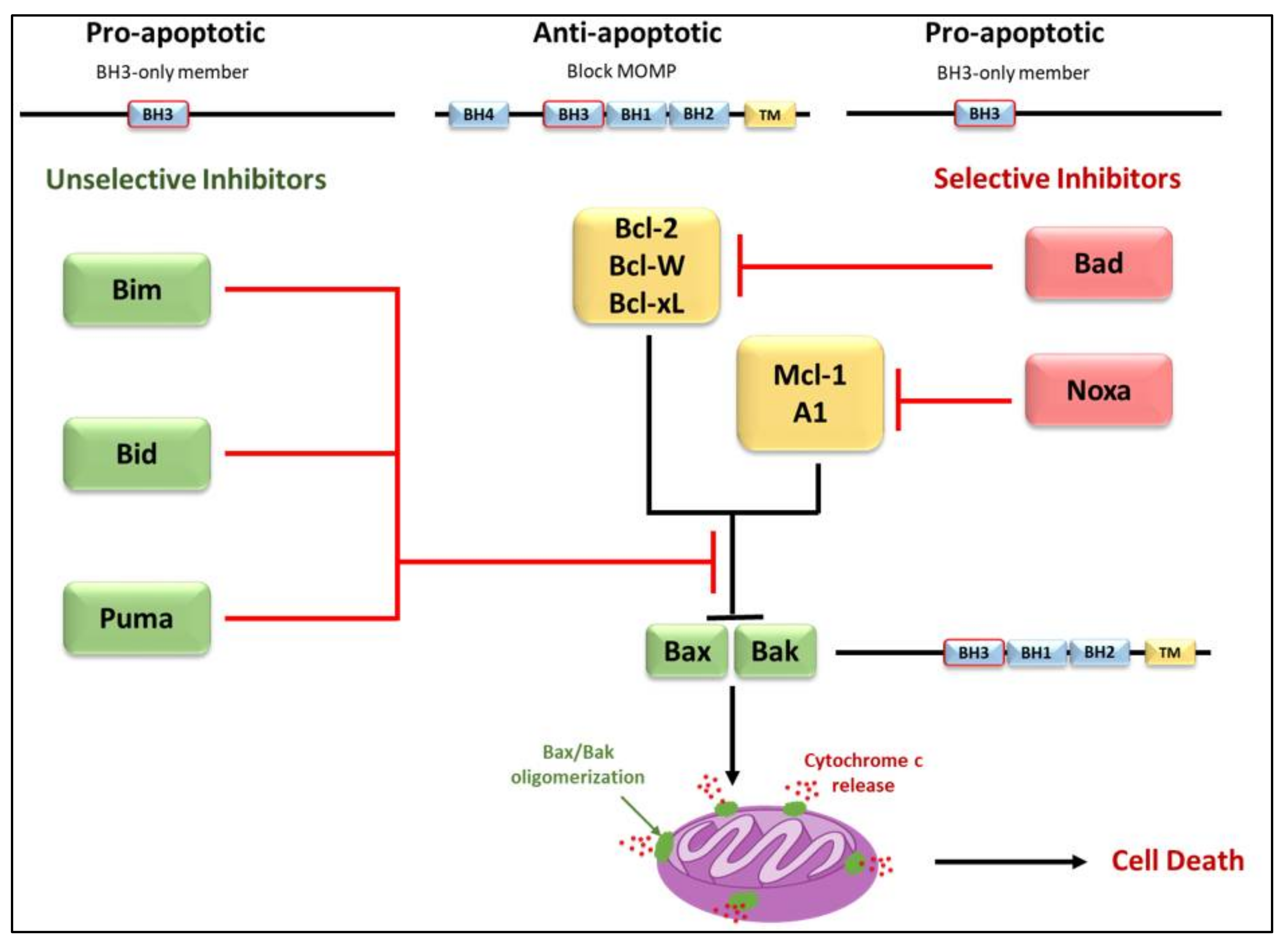
Life, Free Full-Text
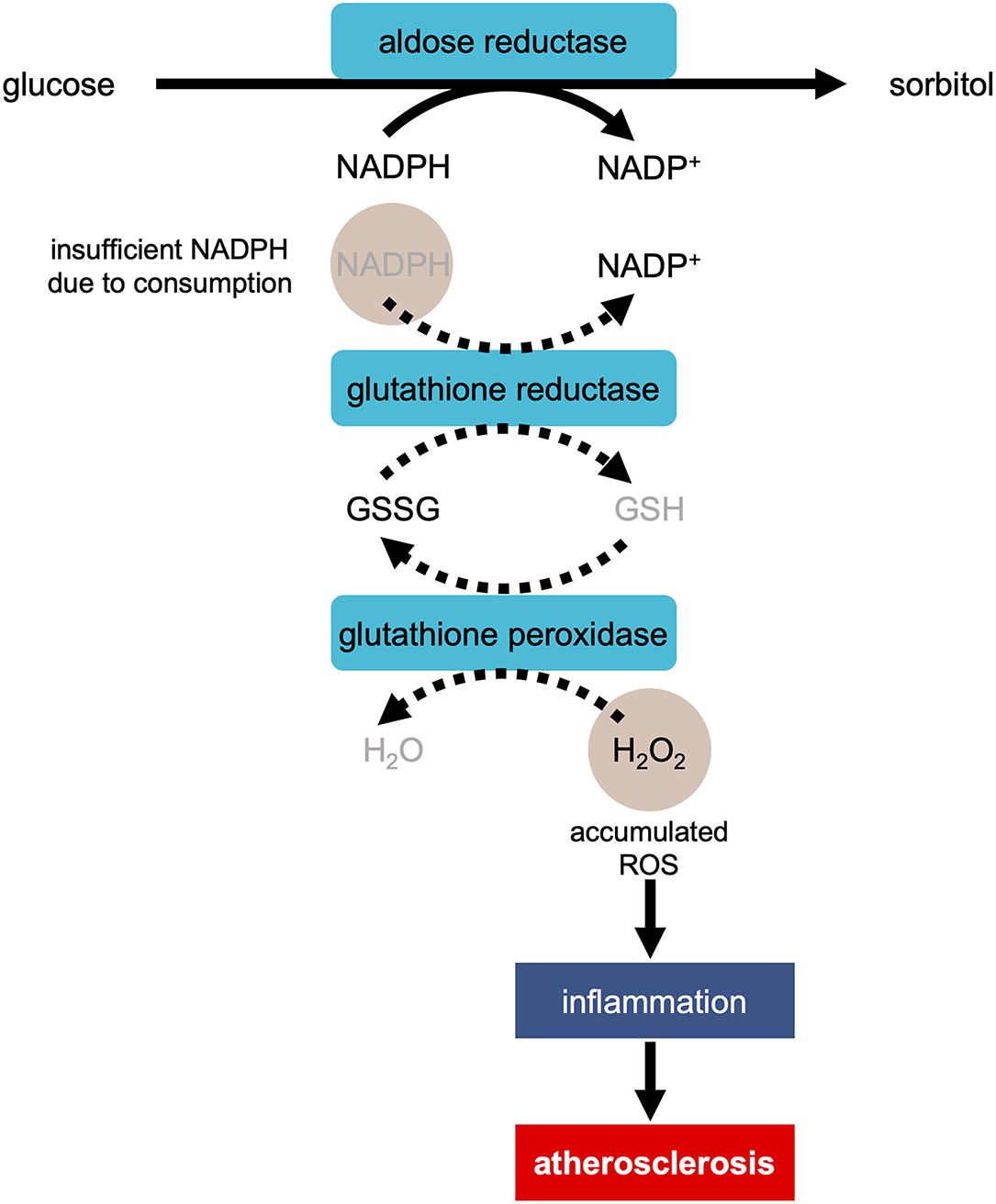
Frontiers Systematic Understanding of Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress-Related Conditions—Diabetes Mellitus, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury

Streptococcus lutetiensis Induces Autophagy via Oxidative Stress in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells

The Snf5‐Hsf1 transcription module synergistically regulates stress responses and pathogenicity by maintaining ROS homeostasis in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum - Xiao - New Phytologist - Wiley Online Library

Streptococcus lutetiensis Induces Autophagy via Oxidative Stress in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells

IJMS, Free Full-Text

Autophagy is a pro-survival adaptive response to heat shock in bovine cumulus-oocyte complexes

Implantable Nanofiber Membranes with Synergistic Photothermal and Autophagy Inhibition Effects for Enhanced Tumor Therapy Efficacy

Biomedicines, Free Full-Text

Heat shock increases levels of reactive oxygen species, autophagy and apoptosis - ScienceDirect
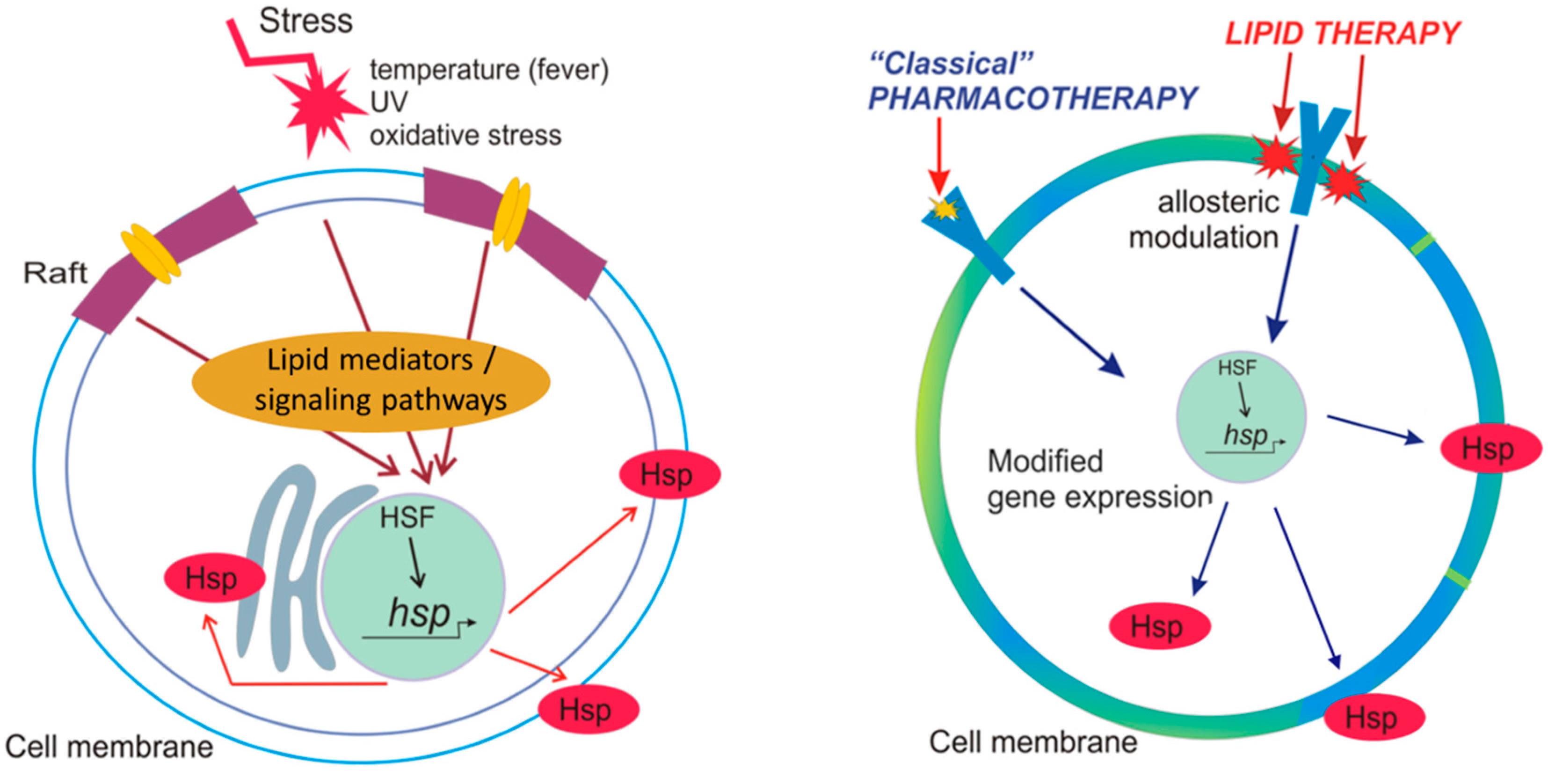
IJMS, Free Full-Text

The Snf5‐Hsf1 transcription module synergistically regulates stress responses and pathogenicity by maintaining ROS homeostasis in Sclerotinia sclerotiorum - Xiao - New Phytologist - Wiley Online Library

Biomedicines, Free Full-Text
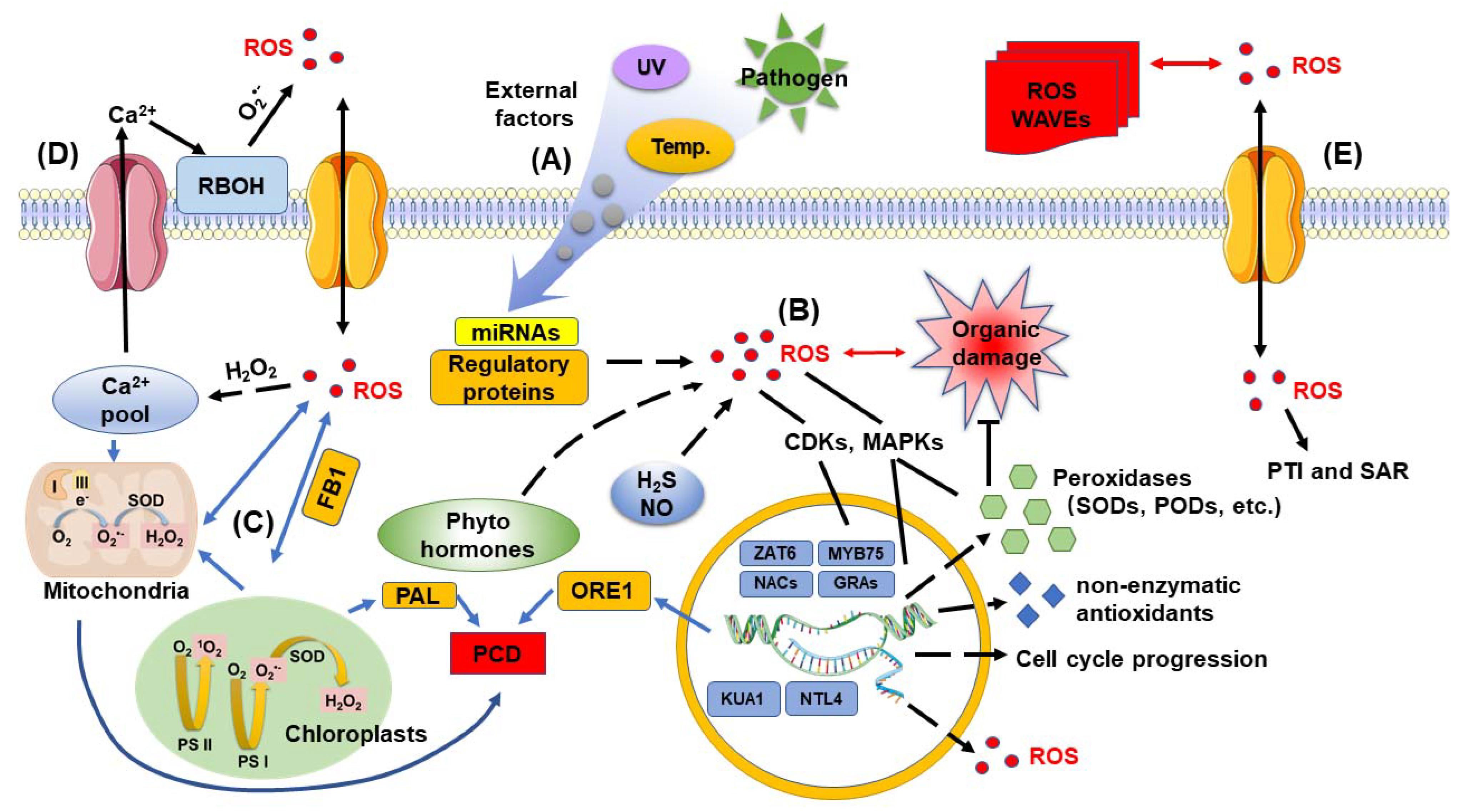
IJMS, Free Full-Text







