Influence of dopants on the structure and catalytic features of
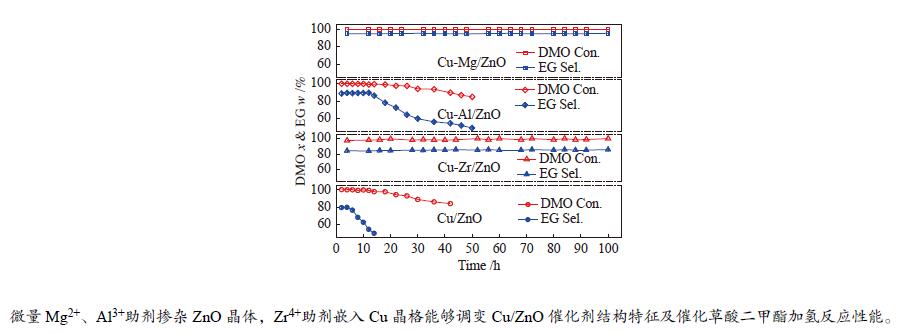
The Cu-<i>M</i>/ZnO catalysts (<i>M</i> = Zr<sup>4+</sup>, Al<sup>3+</sup> and Mg<sup>2+</sup>) for dimethyl oxalate (DMO) selective hydrogenation to ethylene glycol (EG) were synthesized by the co-precipitation method. The properties of the as-synthesized catalysts were characterized by N<sub>2</sub>-physisorption, N<sub>2</sub>O-titration, XRD, H<sub>2</sub>-TPR, CO<sub>2</sub>-TPD, SEM, FT-IR and XPS. It was found that the Cu dispersion could be effectively promoted by the dopants incorporated in the Cu/ZnO catalyst. Particularly, a trace amount of Mg<sup>2+ </sup>and Al<sup>3+</sup> dopants could significantly reinforce the chemical interaction between the Cu and ZnO phases by embedding into the ZnO lattice, while the Cu/ZrO<sub>2 </sub>interaction could be improved with the introduction of Zr<sup>4+</sup>. For DMO gas-phase hydrogenation, the EG yield of the Cu/ZnO catalyst increased from 75.0% to 85.0% and 90.0% in the presence of Zr<sup>4+ </sup>and Al<sup>3+ </sup>dopants, respectively. Particularly, the EG selectivity of Cu-Mg/ZnO catalyst reached up to 95.0% with DMO completely converted for more than 100 h. The correlation between the catalytic behavior and physicochemical features of the Cu/ZnO based catalysts suggested that the surface Cu<sup>+</sup> sites was vital for the catalytic behavior with adequate Cu<sup>0</sup> sites. Additionally, the strengthened Cu/oxide interaction favored the outstanding stability of the Cu-Zr/ZnO and Cu-Mg/ZnO catalyst for DMO hydrogenation.

Influence of dopant substitution mechanism on catalytic properties
Thermogravimetry and differential thermogravimetry (TG-DTG) profiles of

Hydrogenation of ethyl acetate to ethanol over Cu/ZnO/MOx (MOx = SiO2, Al2O3, and ZrO2) catalysts

Review of the Decomposition of Ammonia to Generate Hydrogen
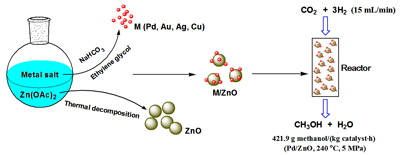
One-Pot Surfactant-Free Synthesis of Transition Metal/ZnO Nanocomposites for Catalytic Hydrogenation of CO2 to Methanol
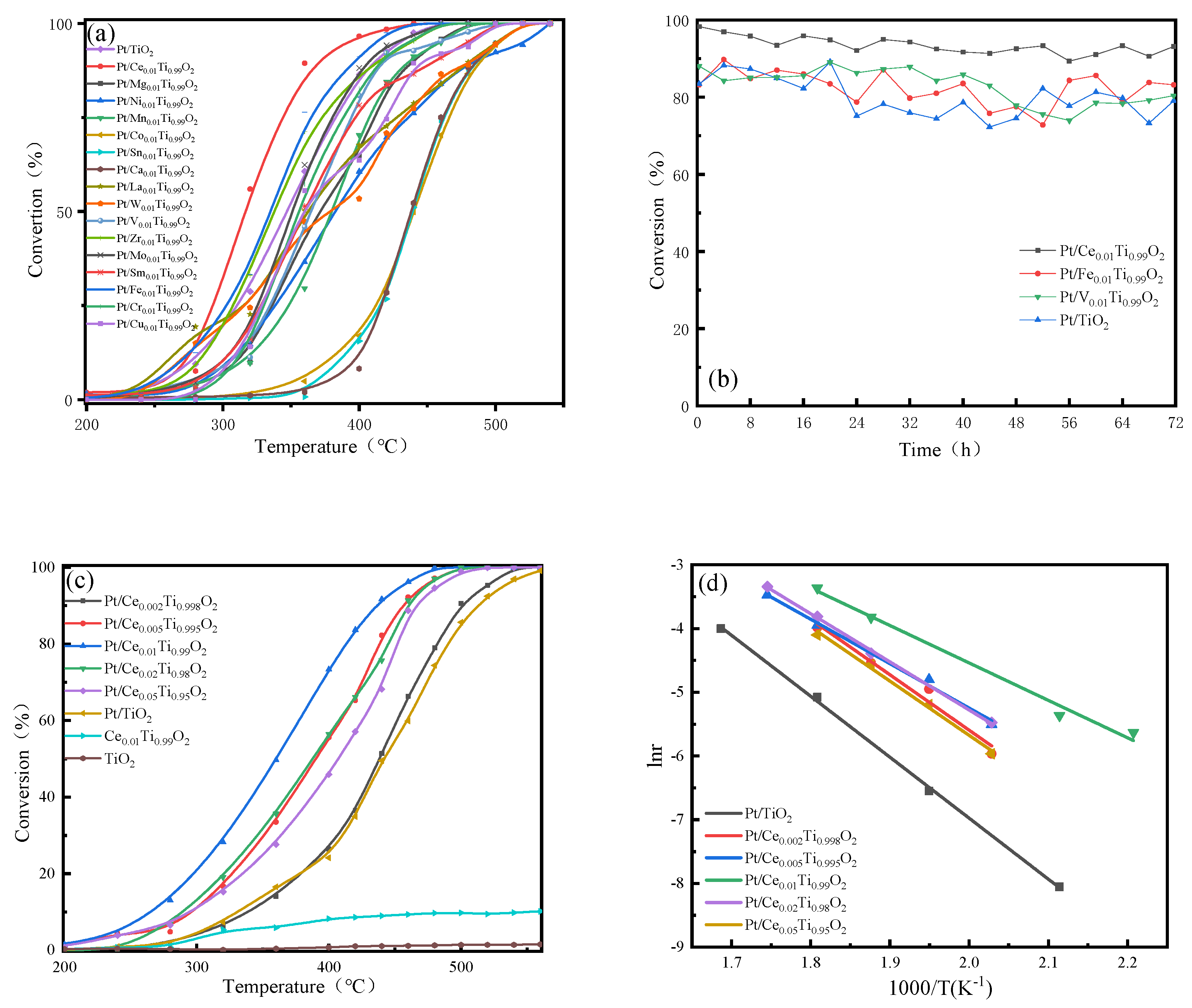
Catalysts, Free Full-Text

PDF) The effect of Al-doping on ZnO nanoparticles applied as catalyst support

Doping Effects on the Performance of Paired Metal Catalysts for

Structural and photoluminescent properties of ZnO hexagonal nanoprisms synthesized by microemulsion with polyvinyl pyrrolidone served as surfactant and passivant - ScienceDirect
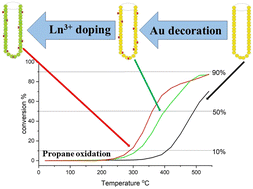
Hierarchical Au/CeO2 systems – influence of Ln3+ dopants on the

CO2-TPD profiles of the reduced Cu–xMg/ZnO catalysts








