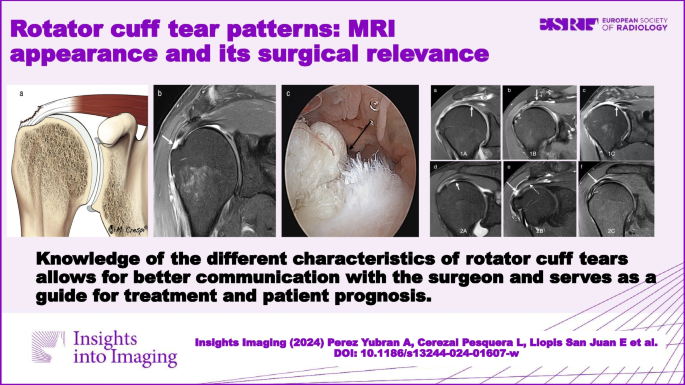
Rotator cuff tear patterns: MRI appearance and its surgical
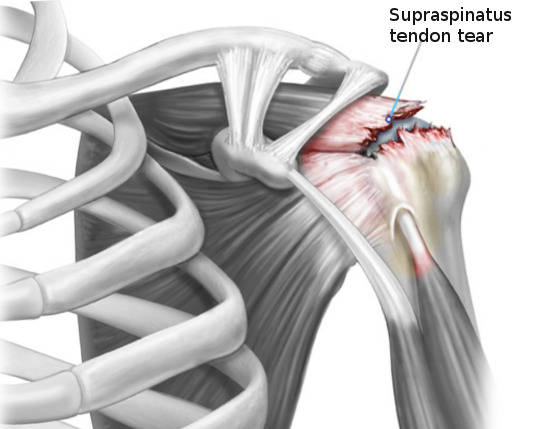
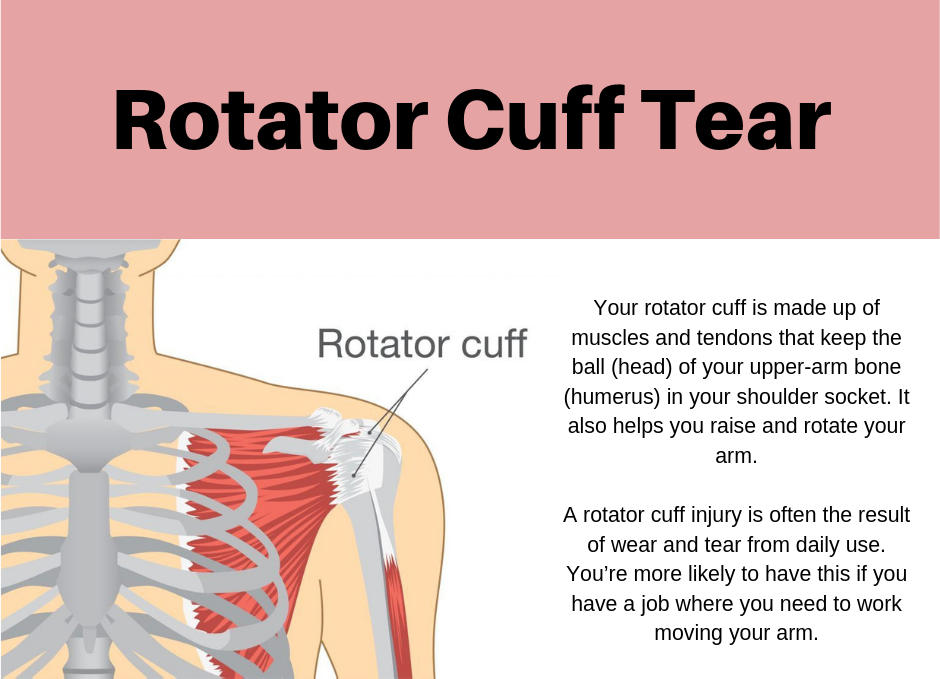
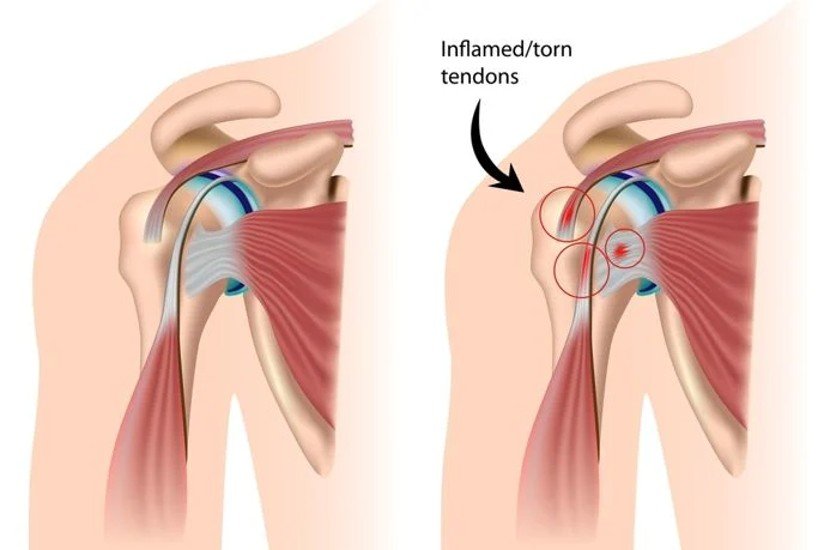
A new perspective on rotator cuff anatomy has allowed a better understanding of the patterns of the different rotator cuff tears. It is essential for radiologists to be aware of these different patterns of tears and to understand how they might influence treatment and surgical approach. Our objective is to review the arthroscopy correlated magnetic resonance imaging appearance of the different types of rotator cuff tears based on current anatomical concepts.Critical relevance statement Knowledge of the characteristics of rotator cuff tears improves our communication with the surgeon and can also make it easier for the radiologist to prepare a report that guides therapeutic conduct and serves as a prognosis for the patient.Key points• There is no universally accepted classification for RC tears.• New patterns such as delamination or myotendinous junction tears have been defined.• The most difficult feature to assess in full thickness tears on MRI is the pattern.• Fatty infiltration of the RC tendons is crucial in the prognosis and outcome.• The radiological report is an effective way of communication with the surgeon. Graphical Abstract

PDF] The geometric classification of rotator cuff tears: a system linking tear pattern to treatment and prognosis.

( A , B ) U-shaped tear. A fluid-filled cuff defect is seen at the

Anterior versus posterior, and rim-rent rotator cuff tears

Figure 5 from Demystifying ABER (ABduction and External Rotation

Different types of rotator cuff tear morphology do not affect post-repair clinical outcomes in large to massive tears - ScienceDirect
Axial and sagittal T2-weighted FATSAT MRI images demonstrating a

Treatment of partial rotator cuff lesions is associated with a

PDF] Rotator cable and rotator interval: anatomy, biomechanics and

Evaluating postoperative rotator cuff healing: Prospective comparison of MRI and ultrasound - ScienceDirect

Rotator Cuff Tear Novus Spine & Pain Center, Lakeland, Florida

Postoperative residual pain is associated with a high magnetic

Acute phase musculotendinous infraspinatus rupture; a: T2 Fat Sat
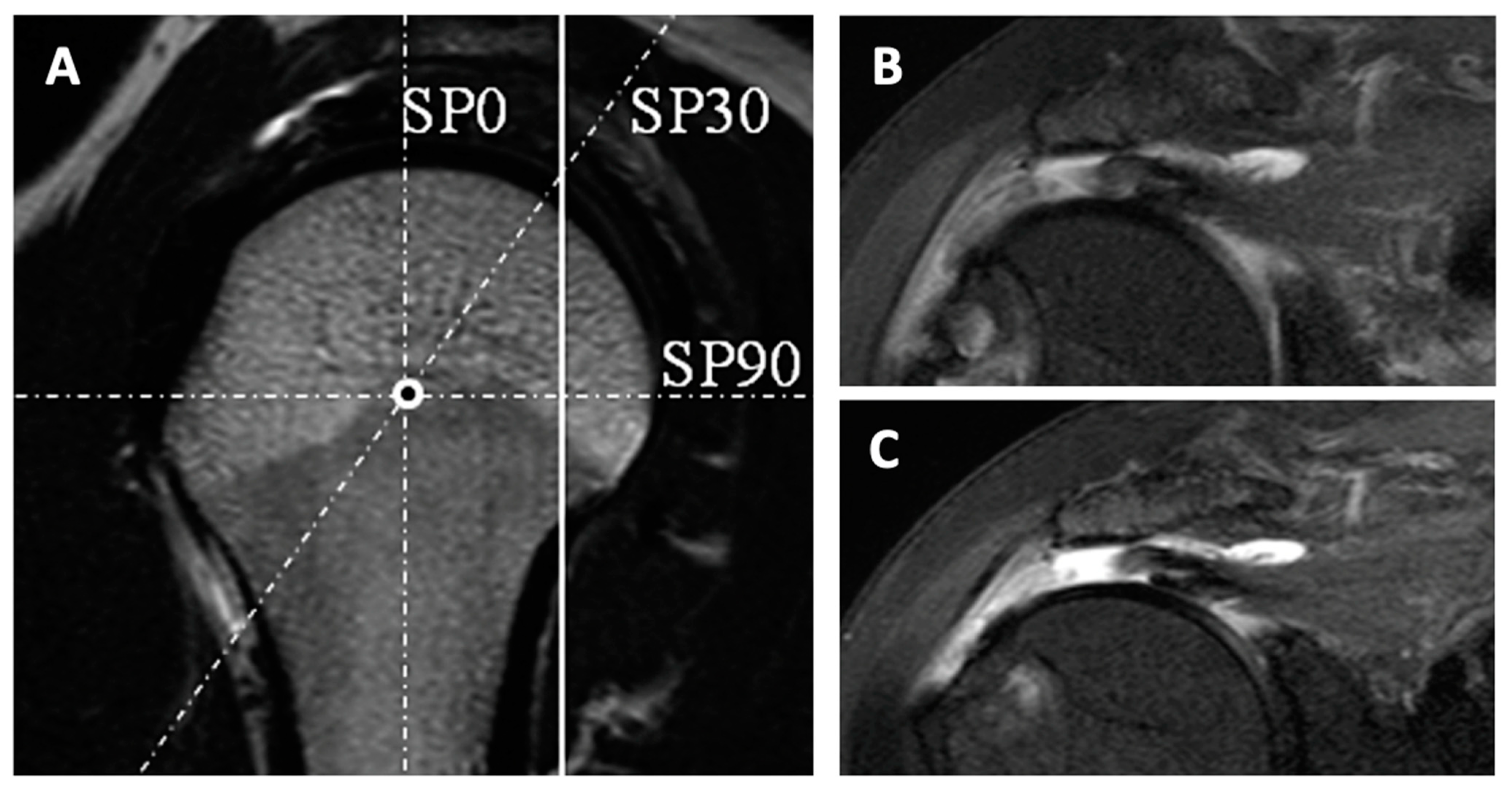
JCM, Free Full-Text