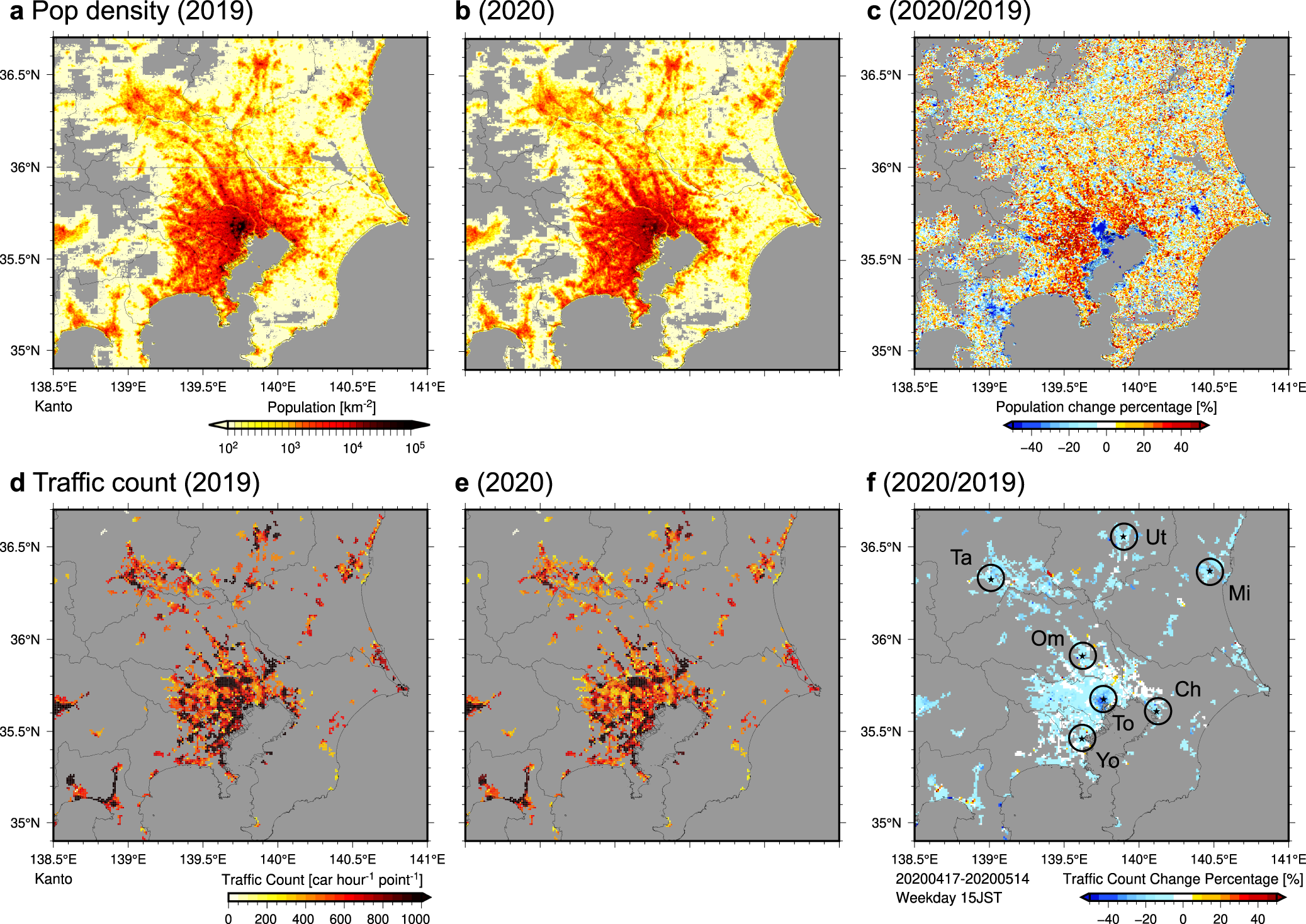
Urban climate changes during the COVID-19 pandemic: integration of urban-building-energy model with social big data

Mean four-week, 1st October–28th October 2014, traffic volume at a

Plots of average diurnal cycles of the observed total CO2 flux, ORF

NH3 emissions from the human body in central Tokyo decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown - ScienceDirect

The differences in monthly nighttime surface air temperature averaged

PDF) Urban climate changes during the COVID-19 pandemic: integration of urban-building-energy model with social big data
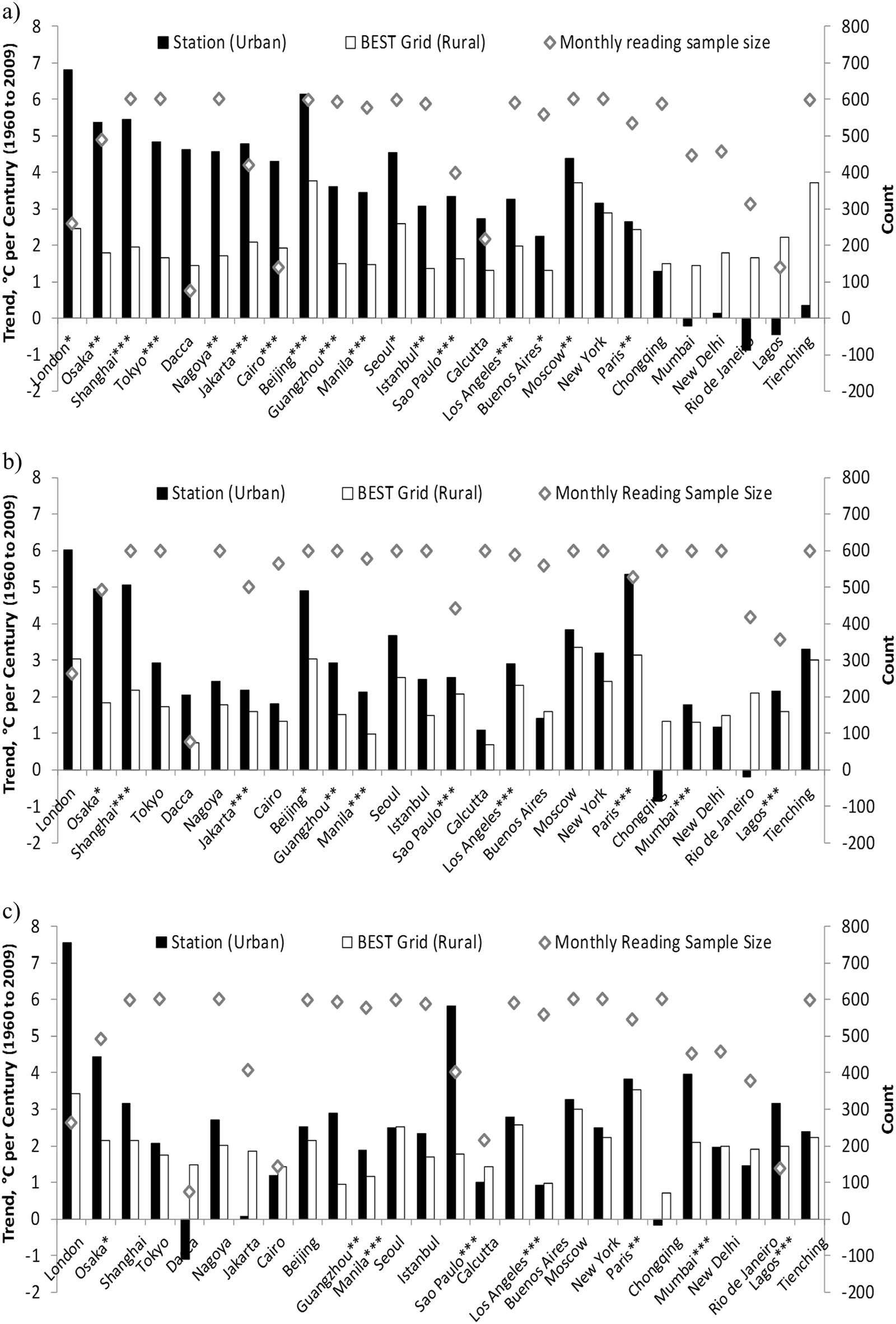
Global urban climatology: a meta-analysis of air temperature trends (1960–2009)
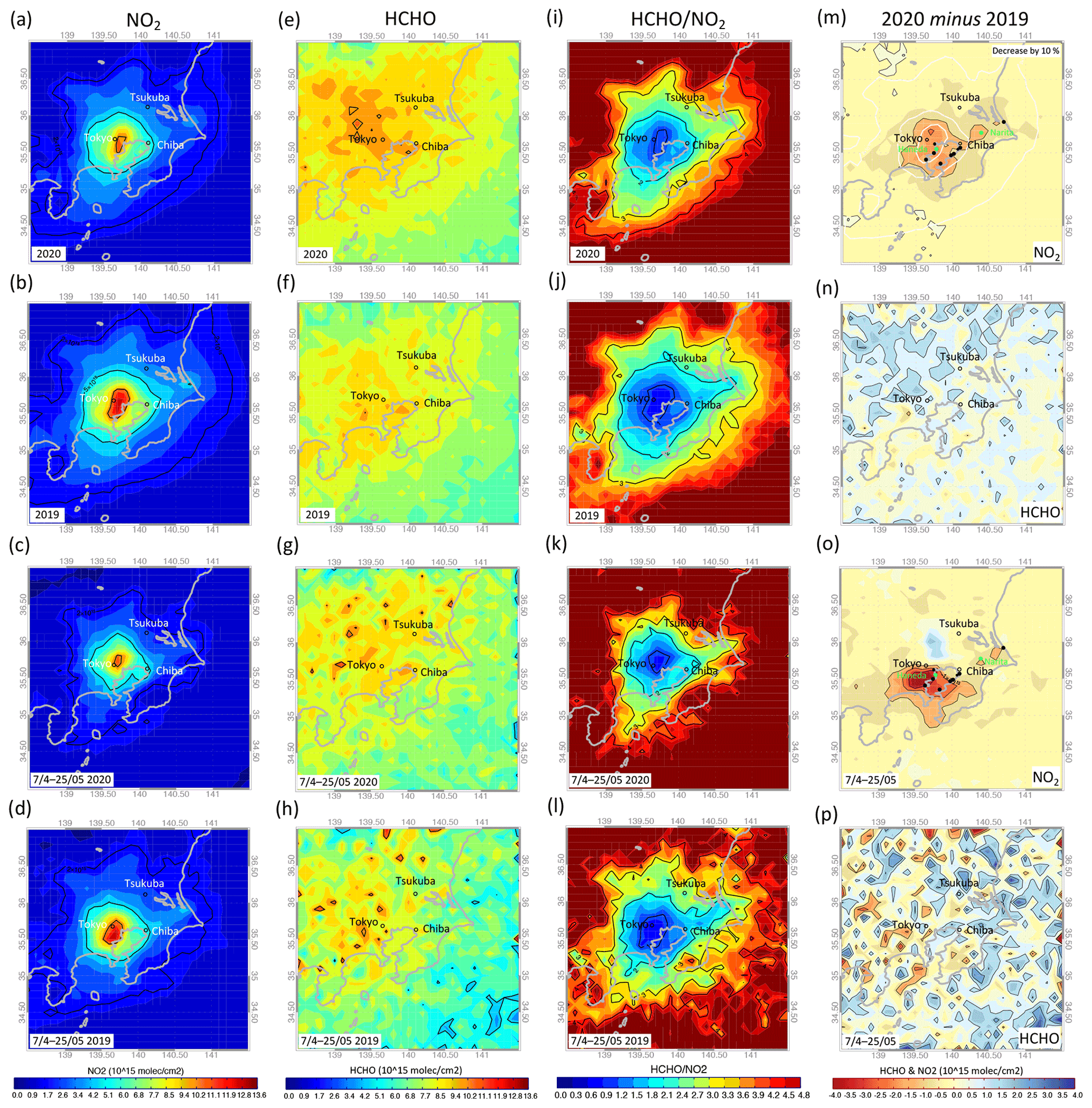
ACP - Peculiar COVID-19 effects in the Greater Tokyo Area revealed by spatiotemporal variabilities of tropospheric gases and light-absorbing aerosols

Spatial distribution of August monthly mean surface air temperature
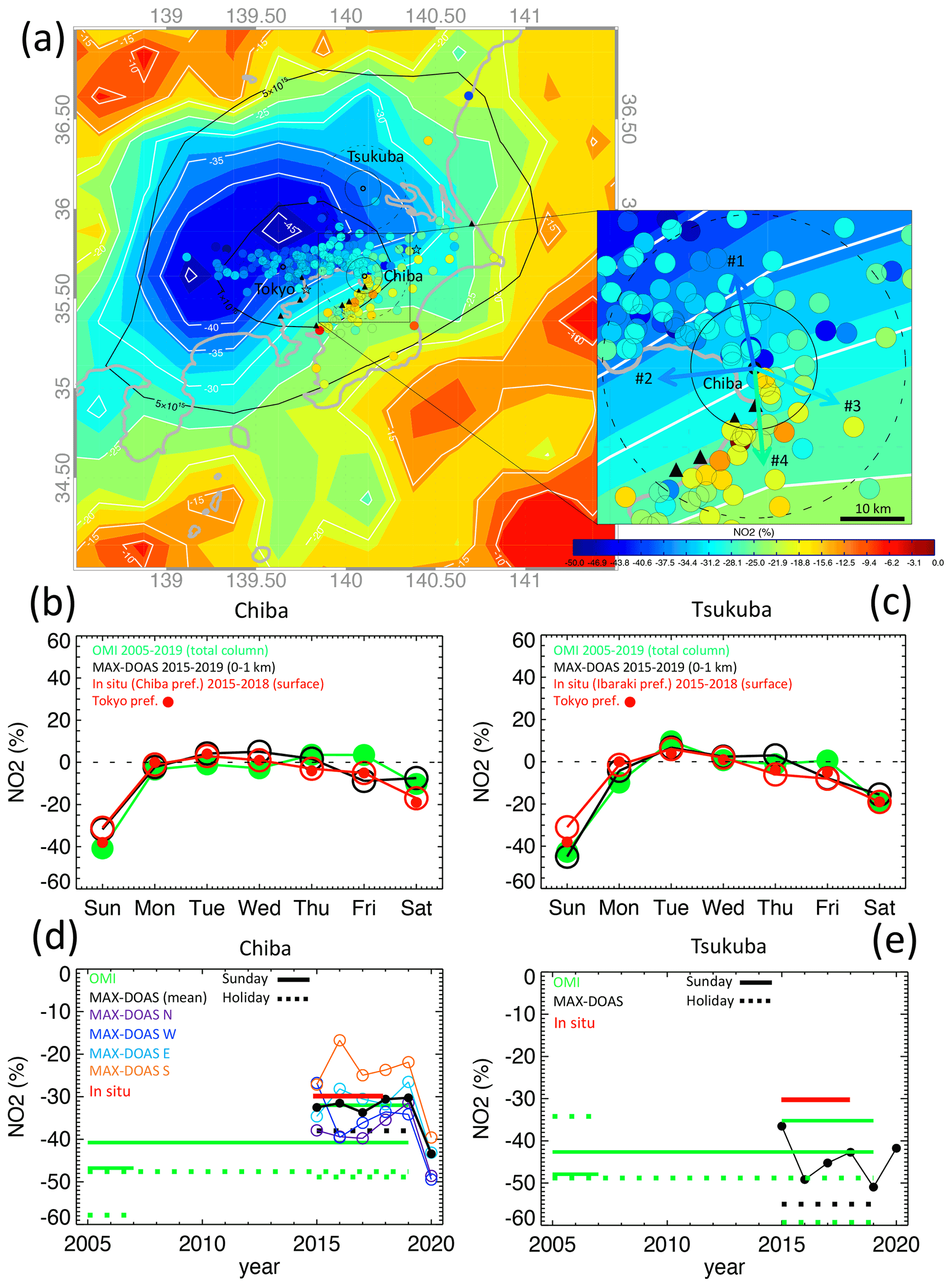
ACP - Peculiar COVID-19 effects in the Greater Tokyo Area revealed by spatiotemporal variabilities of tropospheric gases and light-absorbing aerosols
PDF) Enhancing urban canopy building energy models through the integration of social big data: Improvement and application

Global urban climatology: a meta-analysis of air temperature trends (1960–2009)

Influence of human population movements on urban climate of Beijing during the Chinese New Year holiday

Building heat budget and its response to ΔT in the case of buildings









